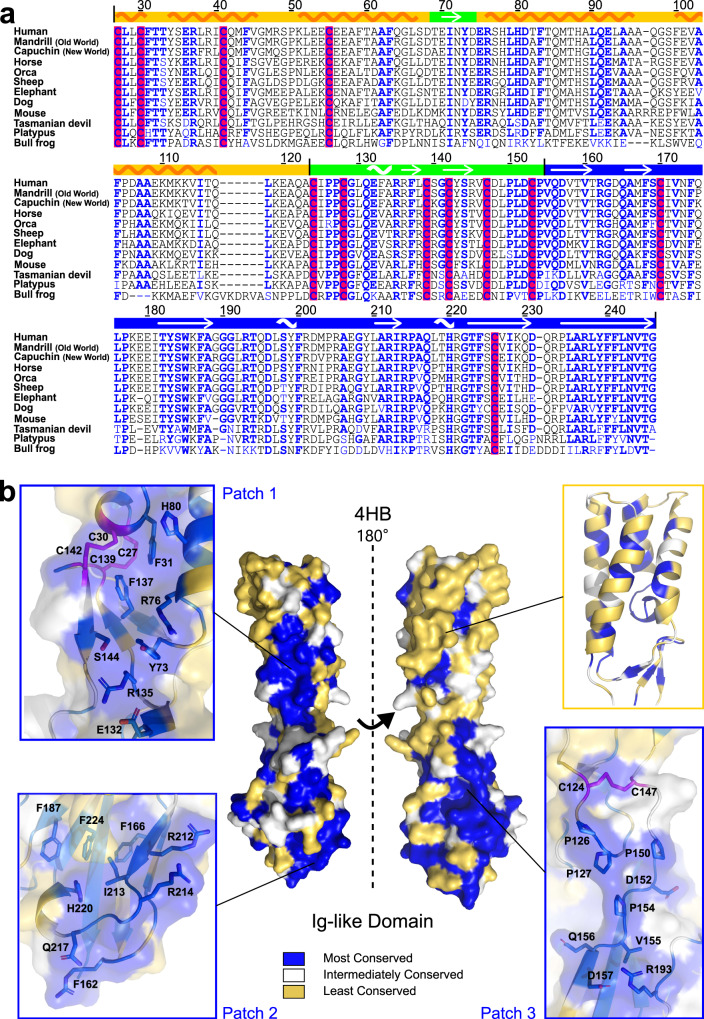
Fig. 6. Conservation of structural elements throughout SPACA6 homologs.
a Sequence alignment of SPACA6 ectodomains from twelve different species prepared using CLUSTAL OMEGA. Most conserved positions according to ConSurf analysis are colored blue. Cysteine residues are highlighted in red. Domain boundaries and secondary structure elements are shown on top of the alignment with arrows indicating beta strands and a wave indicating helices. NCBI accession IDs for included sequences are as follows: human (Homo sapiens, NP_001303901), mandrill (Mandrillus leucophaeus, XP_011821277), capuchin (Cebus imitator, XP_017359366), horse (Equus caballus, XP_023506102), orca (Orcinus orca, XP_012394831), sheep (Ovis aries, XP_014955560), elephant (Loxodonta africana, XP_010585293), dog (Canis lupus familiaris, XP_025277208), mouse (Mus musculus, NP_001156381), Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii, XP_031819146), platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus, XP_039768188), and bull frog (Bufo bufo, XP_040282113). Numbering is based on the human sequence. b Surface representation of the SPACA6 structure oriented with the 4HB at the top and the Ig-like domain at the bottom and colored based on conservation scores from the ConSurf server. Most conserved portions are colored blue, portions with intermediate levels of conservation are white, and least conserved portions are yellow. Cysteines are colored magenta. Three surface patches showing high levels of conservation are shown in the insets labeled Patches 1, 2 and 3. A cartoon representation of the 4HB is shown in top-right inset (same color scheme).