Fig. 5.
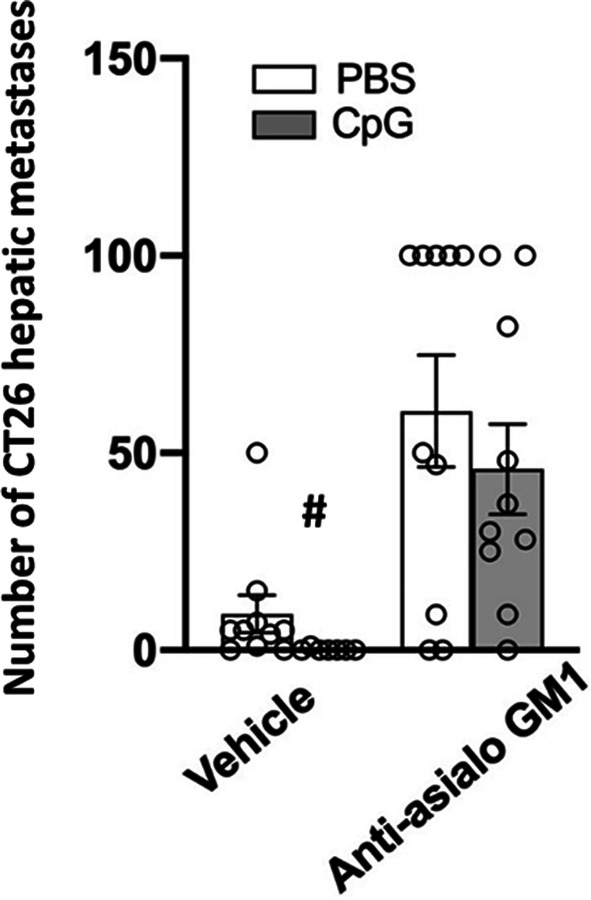
NK cells depletion significantly elevated the number of CT26 surface-hepatic metastases and liver weight, and CpG-C significantly reduced number of metastases in intact mice. A day before tumor inoculation (20,000 cells), female mice were administered with PBS or CpG-C (100 µg/mouse), and were further subdivided to receive PBS or anti-asialo GM1 for NK depletion. NK depletion significantly increased the number of hepatic metastases. In mice with intact NK cells, CpG-C significantly reduced the number of metastases from an average of 10 to 0.1. In NK-depleted mice, CpG-C treatment did not cause a significant reduction in the number of metastases. Data are expressed as mean + SEM. # indicates a significant difference from the PBS
