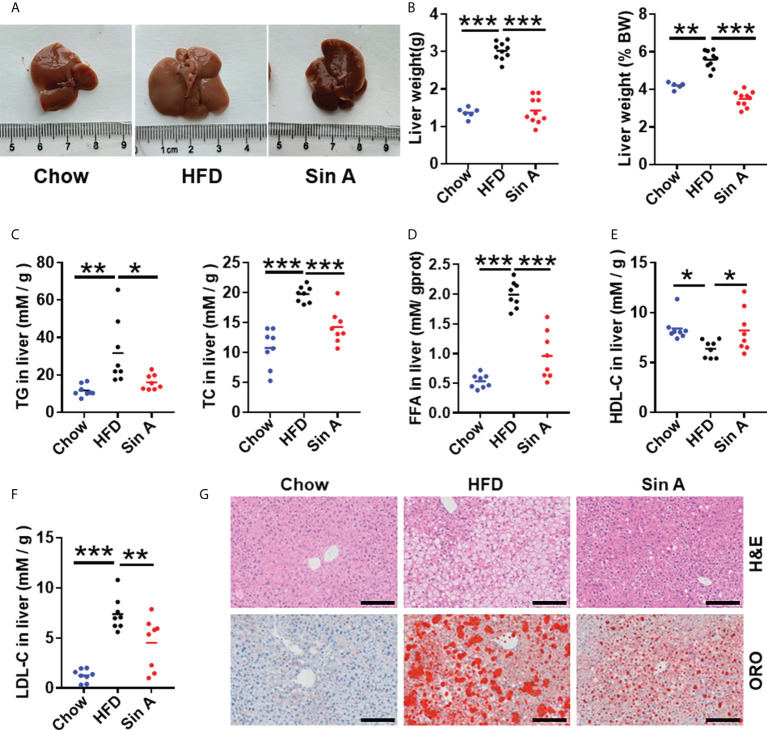
Figure 1.
Sin A attenuates hepatic steatosis in HFD-fed mice. Mice were randomly divided into three groups (n=8–10). Chow diet-fed mice were orally treated with normal diet (chow). HFD-fed mice were orally treated with vehicle (HFD) or Sin A (80 mg/kg) for 6 weeks. (A) Representative images of liver from chow, HFD, and Sin A groups. (B) The result of liver weight and the ratio of liver-to-body weight (BW) (n=6–10 per group). (C) The changes in hepatic triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) (n=8 per group). (D) Free fatty acids (FFAs) contents of liver fraction (n=8 per group). (E,F) Changes in liver HDL-C, LDL-C level. (G) Representative images of H&E staining and Oil Red O staining of liver. Scale bars 100 μm. Values represent mean ± SD. Significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA for multiple- group comparisons. p*<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; FFA, free fatty acid; ORO, Oil Red O staining.