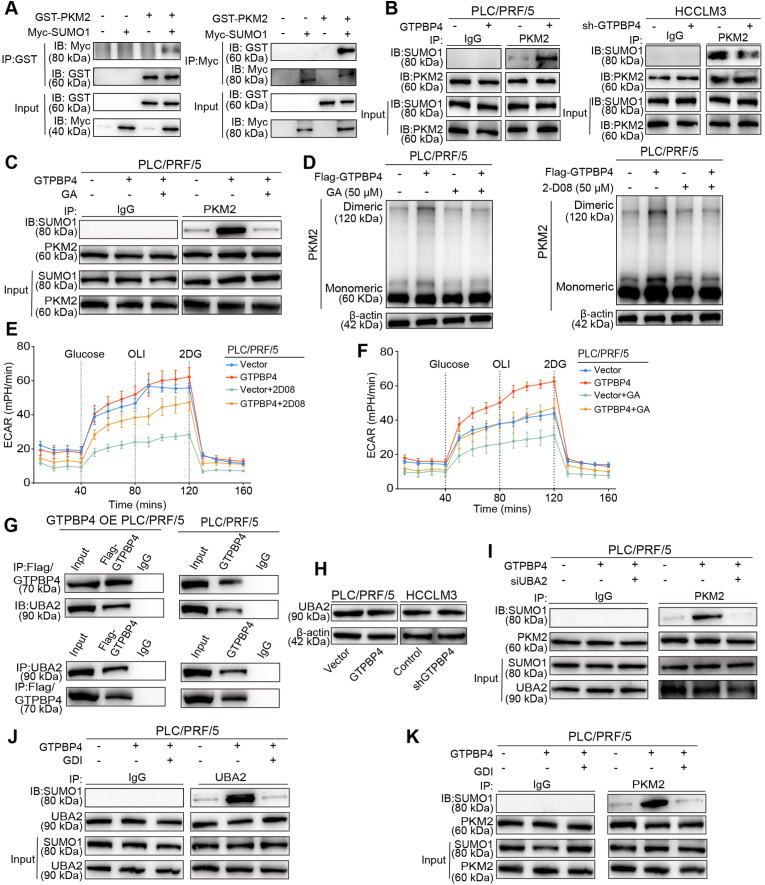
Fig. 5.
GTPBP4 induces PKM2 protein sumoylation and dimer formation through UBA2/SUMO1 axis. (A) IP and Western blot were performed to assess PKM2 sumoylation in HEK-293T cells. n = 3. (B) IP and Western blot analyses were performed to assess PKM2 sumoylation in GTPBP4 OE PLC/PRF/5 and GTPBP4 KD HCCLM3 cells compared with the respective controls. n = 3. (C) sumoylation inhibitors, GA (50 μM) could inhibit GTPBP4-induced PKM2 protein Sumoylation. n = 3. (D) Monomeric and dimeric PKM2 expression were analyzed using Western blot in PLC/PRF/5 cells with or without GTPBP4 overexpression in the presence of Sumoylation inhibitors, GA (50 μM) and 2-D08 (50 μM). n = 3. (E–F) ECAR were detected in GTPBP4 OE PLC/PRF/5 and control cells in the presence of sumoylation inhibitors, GA and 2-D08. n = 6. (G) GTPBP4 and UBA2 co-localization were determined by Co-IP assays. (H) GTPBP4 has no effect on UBA2 protein expression. n = 3. (I) UBA2 knockdown could inhibit GTPBP4-induced PKM2 Sumoylation. n = 3. (J) GDI could significantly inhibit the activation of SUMO1 protein by GTPBP4 overexpression through UBA2. n = 3. (K) GDI could significantly inhibit the GTPBP4-induced PKM2 protein Sumoylation. n = 3. The data presented in (E)–(F) are compared among groups using one-way ANOVA. Error bars represent the mean ± SD from six independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001.