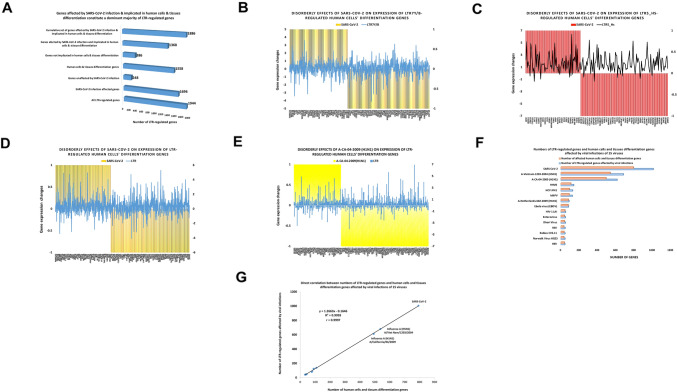
Fig. 13.
A dominant majority of high-confidence LTR-regulated down-stream target genes constitutes genes expression of which is affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection and defined as genetic markers of differentiation of multiple types of human cells and tissues. Panel A reports the number of genes expression of which is affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection (1696 genes); the number of genes defined as genetic markers of differentiation of human cells and tissues (1558 genes); the number of genes assigned to both viral infection and cellular differentiation categories (1368 genes); and the cumulative number of genes identified as SARS-CoV-2 infection targets and/or human cells’ and tissues’ differentiation genes (1886 genes) among 1944 genes comprising high-confidence down-stream regulatory targets of retroviral LTRs. Panels B–E illustrate disorderly effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection (B–D) and influenza H1N1 strain A-CA-04-2009 (H1N1) infection (E) on expression of LTR-regulated human cells’ and tissues’ differentiation genes. Panels F, G summarize the experimental evidence documenting a strict direct correlation between the numbers of LTR-regulated human cells’ and tissues’ differentiation genes and the numbers of LTR-regulated genes expression of which is significantly affected by viral infections of 15 different viruses