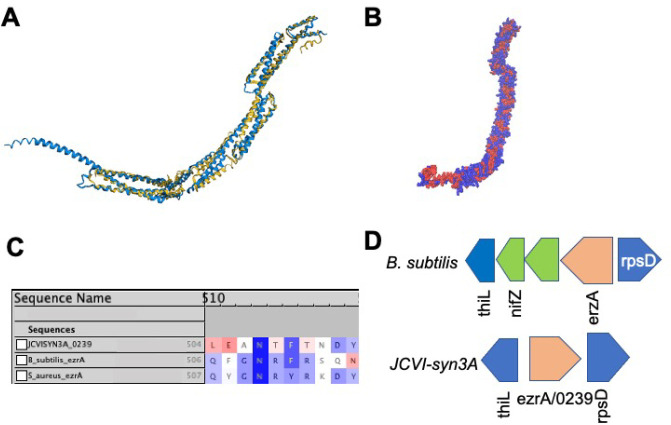
Figure 2.
(A) Structural alignment by FATCAT25 of the predicted AlphaFold2 structure for gene /0239 (blue) to the structure of the cell division regulatory protein EzrA from B. subtilis (yellow, RCSB PDB: 4UXV(65)) with 498 or 84% of the residues of /0239 being well-aligned to the experimental structure with a p-value of 3.01 × 10–10 for significant structural similarity. (B) Hydrophobicity coloring (red, hydrophobic resiudes; blue, hydrophilic residues) for the AlphaFold2 predicted structure for /0239. Hydrophobic regions at the N and C termini match the previous findings that EzrA binds the membrane at each terminal domain.65 (C) Sequence Alignment of gene /0239 with the sequences for ezrA from S. aureus and B. subtilis with BLOSUM50 similarity score coloring. While the entire characteristic “QNR” patch63,64 is not present in JCVI-syn3A, significant sequence similarity remains and the nearly universally conserved asparagine residue located centrally in the patch is present. (D) The genome architecture of JCVI-syn3A also lends support to the assignment of ezrA/0239. Just as in the related Gram-positive organism B. subtilis, the gene coding for EzrA lies between the genes for thiL coding for thiamine monophosphate kinase and rpsD coding for ribosomal protein S2 on opposing strands of the circular genome.