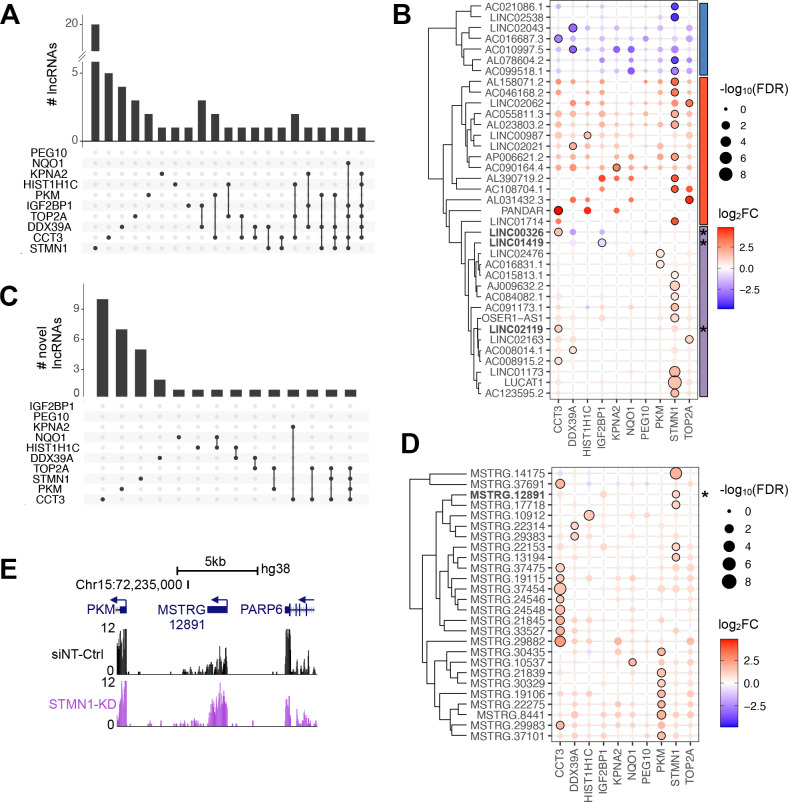
Figure 3.
RBP-KD affects lincRNA gene expression levels. (A, C) Bar graph show the number of (A) annotated and (C) novel DE lincRNA genes detectable after RBP-KDs. The frequency of lincRNA genes in one (black dot) or multiple (black dots connected by a line) RBP-KD experiments is shown. (B, D) Circle plots display the occurrence of (B) annotated and (D) novel lincRNA genes per RBP-KD. The diameter of the circles corresponds to varying degrees of significance (large: high, and narrow: low FDR value, black line: FDR<0.05). The colour code represents fold change (red: upregulated and blue: downregulated). Vertical bars specify the three most common clusters defining lincRNAs as either consistently downregulated (blue) or upregulated (red), or with varying pattern deregulation across the ten RBP-KD (purple). A star (*) marks lincRNAs used for further investigation. (E) The UCSC genome browser view demonstrates the genomic location of the novel lincRNA MSTRG.12891 in between genes encoding for PKM and PARP6. Arrows indicate direction of gene transcription. Gene expression patterns in Huh7 cells transfected with siNT-Ctrl (black) or siRNA-mediated KD of STMN1 (purple) are shown. The y-axis of each track specifies normalised RNA-seq read intensity.