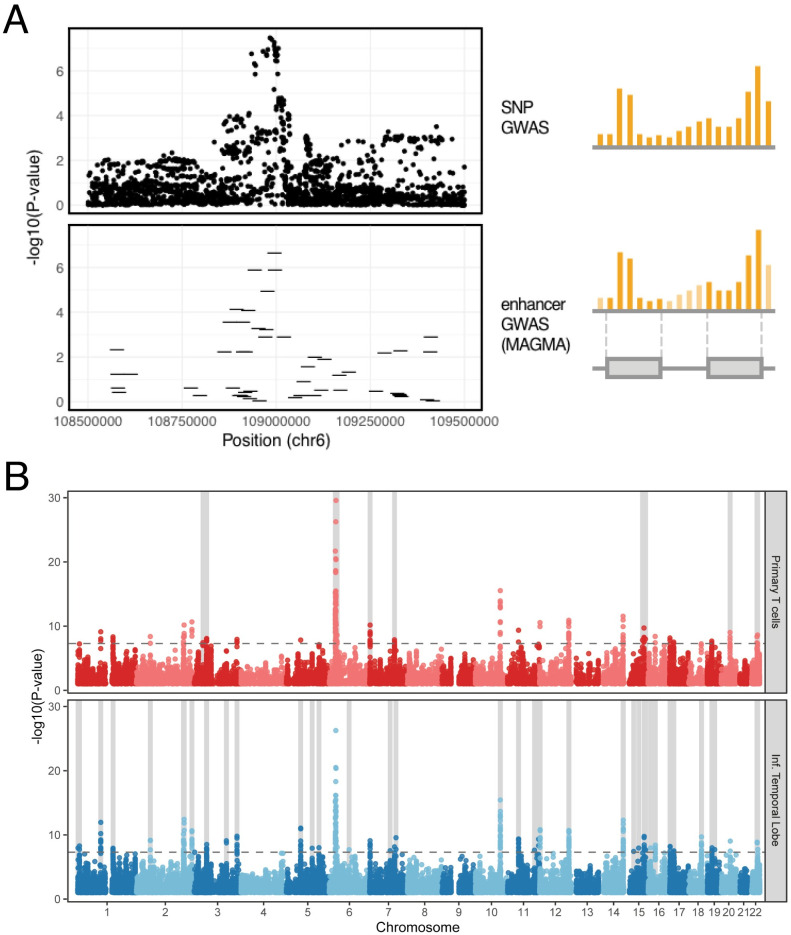
Fig 4. Identification of brain-expressed enhancers associated with genetic risk for schizophrenia.
A) Enhancer-based GWAS allows the aggregation of non-coding SNPs into nearby enhancer regions and captures risk loci as enhancer-level risk associations. Individual points on the top panel denote SNPs, while the lines on the bottom panel represent enhancer regions. B) Brain enhancers capture risk loci missed by enhancers from other tissues. Enhancers from primary T cells captured fewer genome-wide significant signals when compared to enhancers from the inferior temporal lobe of the adult brain. The light gray shaded areas denote loci where a given enhancer annotation has more genome-wide significant enhancers when compared to the other annotation.