Figure 7. Thpok-NuRD binding is needed for Runx3 repression.
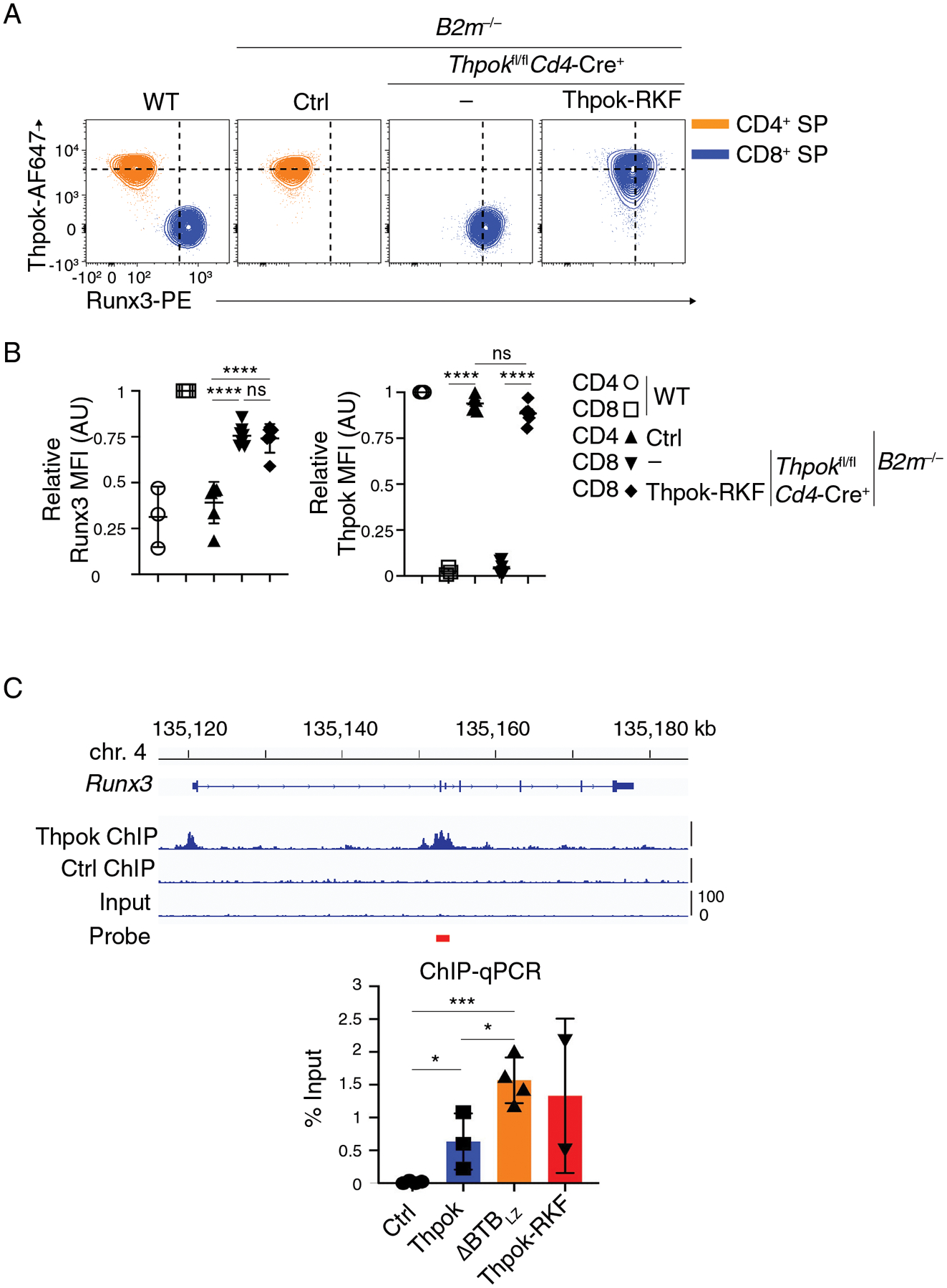
(A) Flow cytometric expression of intra-cellular Runx3 and Thpok in CD44lo CD24lo TCRβhi CD4+ SP (orange traces) or CD8+ SP (blue traces) thymocytes from indicated mice.
(B) (Left panel) Expression of Runx3 in CD44lo CD24lo TCRβhi CD4+ SP or CD8+ SP thymocytes is presented relative to that of CD44lo CD24lo TCRβhi CD8+ SP in WT mice, set as 1 in each experiment. (Right panel) Expression of transgenic Thpok-RKF in CD44lo CD24lo TCRβhi CD4+ SP or CD8+ SP thymocytes is presented relative to that of endogenous Thpok in CD44lo CD24lo TCRβhi CD4+ SP in WT mice, set as 1 in each experiment. One-way ANOVA followed with Tukey multiple comparison tests. ****p<0.0001, ns: p>0.05. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Data (A, B) are representative of three independent experiments totaling n= 3 (WT), 6 (Cd4-Cre− Thpokfl/fl B2m−/−), 7 (Cd4-Cre+ Thpokfl/fl B2m−/−) or 6 (Cd4-Cre+ Thpokfl/fl B2m−/− Thpok-RKF+) mice.
(C) (Top) Thpok or Ctrl ChIP-seq traces on the Runx3 loci in activated CD4 T cells (42); the red bar schematizes the PCR probe in experiments below. (Bottom) Bar graph quantifies streptavidin-ChIP of activated CD4+ T cells from Thpokfl/fl Ox40-Cre+ Rosa26BirA+ mice that had been retrovirally transduced with empty pMRx (Ctrl) or with pMRx expressing Thpok-Bio, ΔBTBLZ-Bio or Thpok-RKF-Bio. Data shows the amount of PCR-amplified DNA, expressed as percent of input. Each symbol represents a separate determination, and the figure summarizes three distinct experiments. Unpaired t test. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
