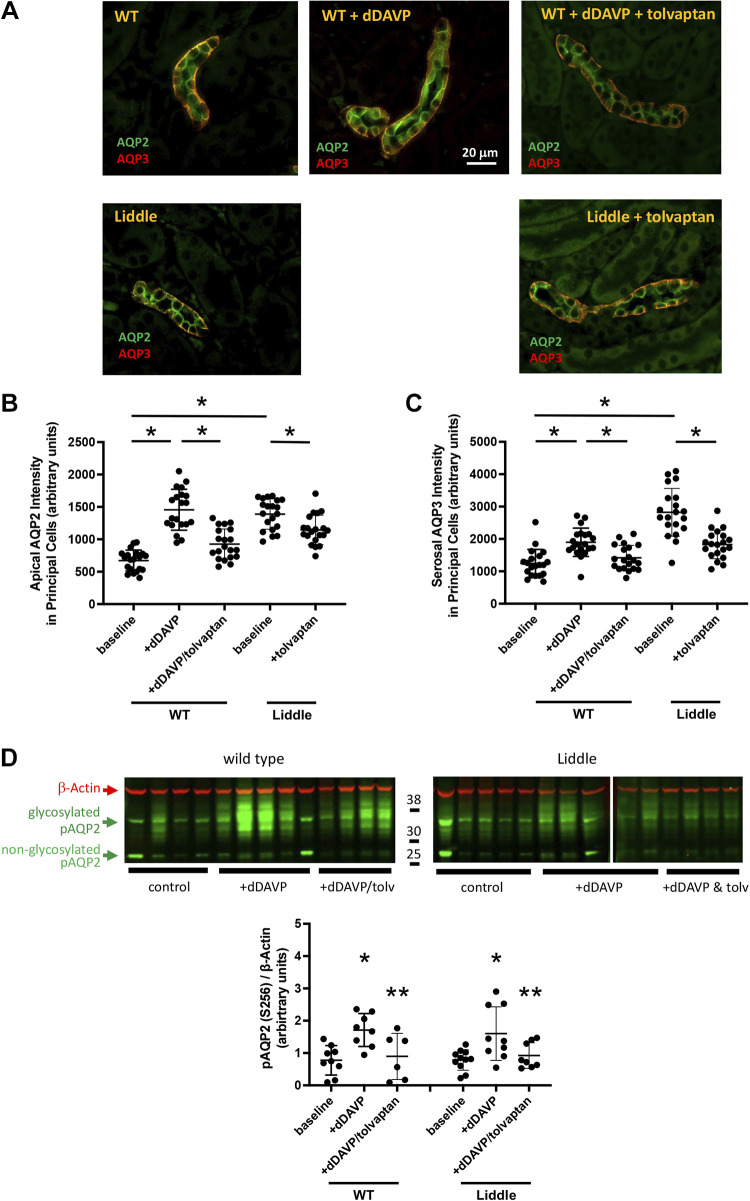
Figure 2.
Expression of aquaporin-2 (AQP2) and aquaporin-3 (AQP3) in the collecting duct is high in Liddle mice. A: representative kidney sections of wild-type (WT) and Liddle male mice. Red fluorescence indicates AQP2 expression; green fluorescence indicates AQP3 expression. Expression of AQP2 was in the apical membrane and expression of AQP3 was in the serosal membrane of collecting ducts of WT and Liddle mice. Mice were infused with desmopressin (dDAVP) in the absence or presence of the V2 receptor antagonist tolvaptan, as indicated. B: apical expression of AQP2 was significantly higher in principal cells of the collecting ducts of Liddle mice compared with WT mice. Means (±SE) apical AQP2 intensity was from n = 20 random cells for each group, analyzed from 5 kidney sections from 4 different mice. *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction between the indicated groups. C: serosal expression of AQP3 was significantly higher in principal cells of the collecting ducts of Liddle mice compared with WT mice. Means (±SE) serosal AQP3 intensity was from n = 20 random cells for each group, analyzed from 5 kidney sections from 4 different mice. *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction between the indicated groups. D: Liddle mice responded to V2 receptor stimulation and inhibition to a similar extent as WT mice. Male or female mice were treated with vehicle control, dDAVP, and dDAVP with tolvaptan. Immunoblots of kidney lysates were probed with antibodies directed against phospho-AQP2 (Ser256; pAQP2) and β-actin. Means (±SE) densitometric analysis for expression of pAQP2 was normalized to the expression of β-actin in kidney lysates from WT and Liddle mice. *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction between dDAVP and vehicle control. **P < 0.05 between dDAVP and dDAVP + tolvaptan. n = 6−11 mice for each group as indicated.