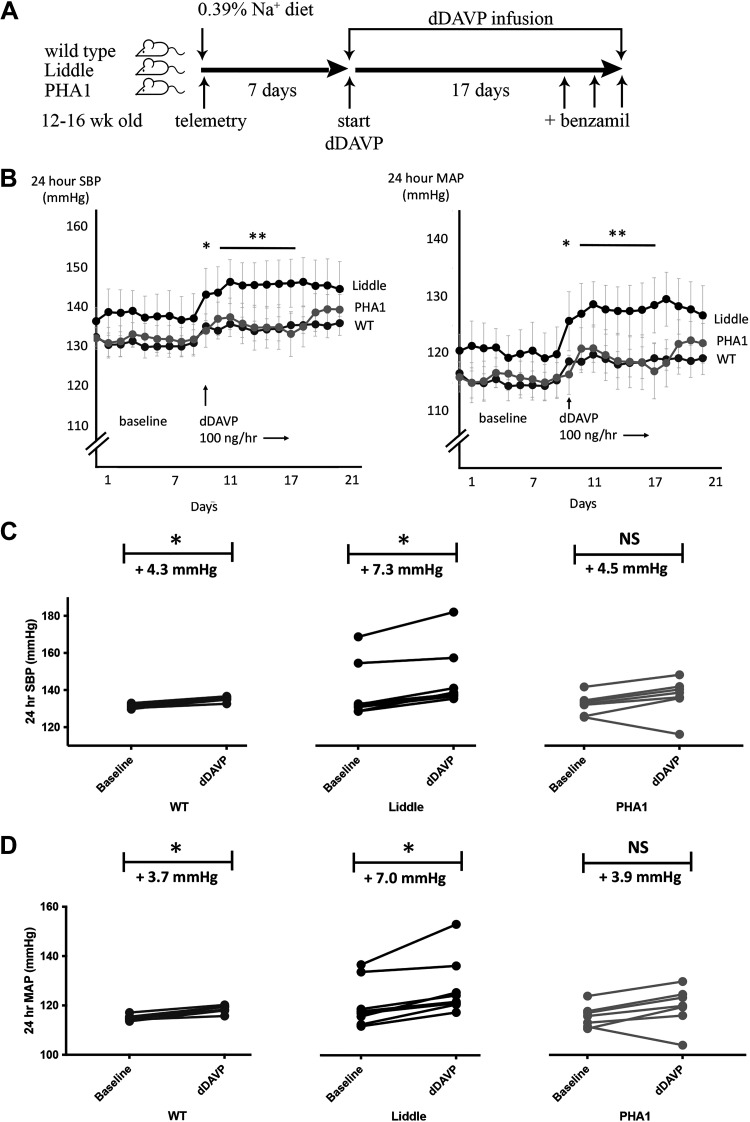
Figure 3.
Chronic infusion of desmopressin (dDAVP) increases blood pressure in wild-type (WT) and Liddle mice. A: experimental scheme. After mice were fed a regular chow diet for 7 days, they received infusion of dDAVP (100 ng/h) for 14 days. Benzamil was administered to mice on the last 3 days of the experiment. B: radiotelemetric measurement of means (±SE) systolic blood pressure (SBP) or mean arterial pressure (MAP) before and after chronic infusion of dDAVP in male WT, Liddle, and pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (PHA1) mice. *P < 0.05 by Kruskal–Wallis test for SBP or MAP between baseline and dDAVP for Liddle and WT mice. **P < 0.05 by Kruskal–Wallis test for SBP or MAP during days 11−17 (during days 2−8 of dDAVP infusion) for dDAVP-infused Liddle mice vs. SBP or MAP in other groups of dDAVP-infused mice. C: SBP response to chronic dDAVP infusion. Baseline represents the average of SBP of mice from days 1−7; dDAVP represents the average SBP of mice from days 11−21. *P < 0.05 vs. baseline by a Kruskal–Wallis test. n = 7 WT mice, 8 Liddle mice, and 7 PHA1 mice. D: MAP response to chronic dDAVP infusion. Baseline represents the average of MAP of mice from days 1−7; dDAVP represents the average MAP of mice from days 11−21. *P < 0.05 vs. baseline by a Kruskal–Wallis test. n = 7 WT mice, 8 Liddle mice, and 7 PHA1 mice.