Figure 1.
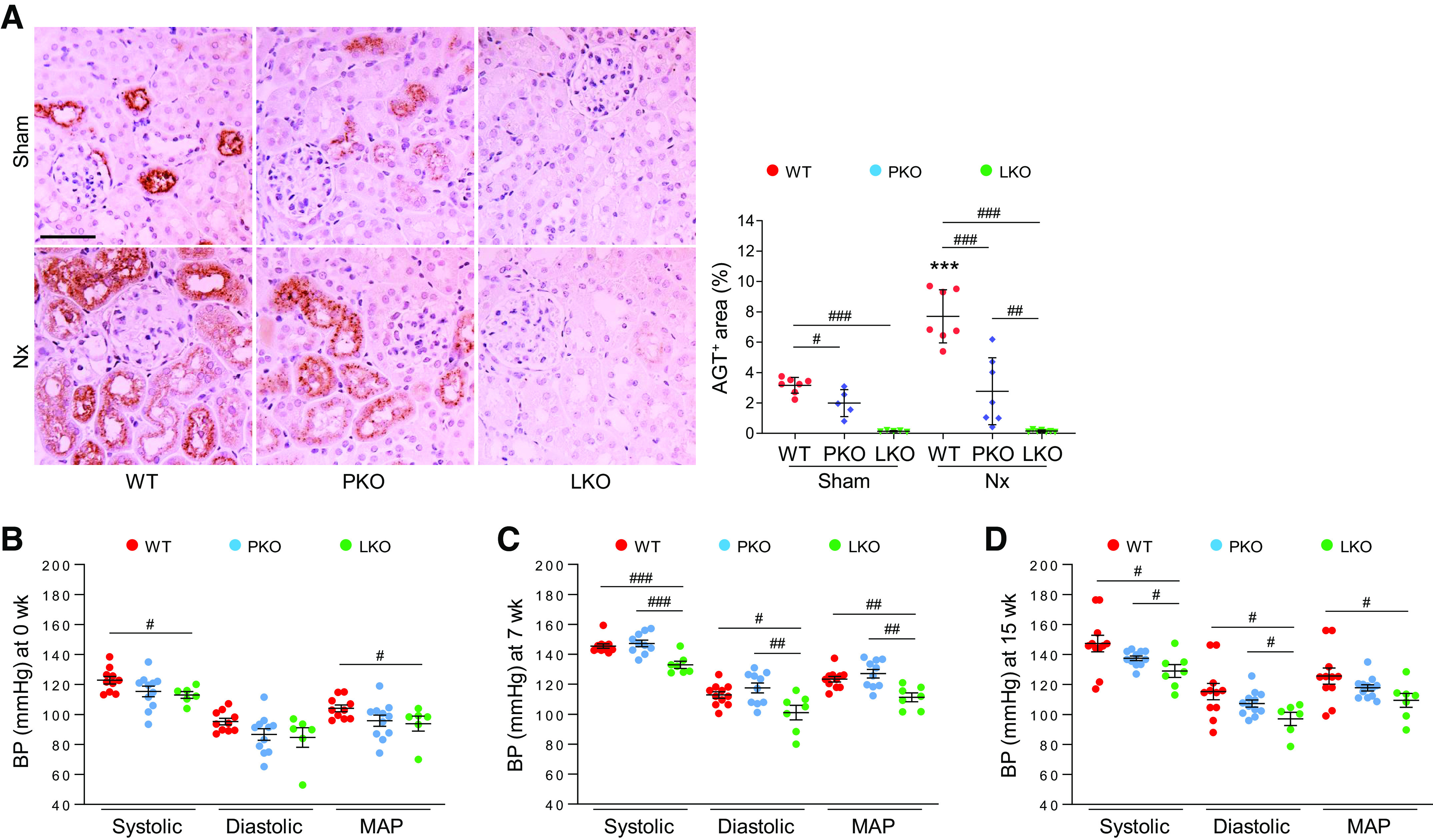
Contribution of tissue-specific angiotensinogen (AGT) in renal AGT expression and its role in blood pressure (BP) regulation during chronic kidney disease. 5/6 Nephrectomy (Nx) in wild-type (WT), proximal tubule-specific AGT knockout (PKO), and liver-specific AGT knockout (LKO) mice was induced by a two-step procedure as described in materials and methods. Mice were harvested 16 wk post-Nx. A: paraffin-embedded kidney sections were used to carry out immunohistochemistry for evaluating AGT. Data were quantified from five randomly chosen fields per kidney using ImageJ software (n = 5–7). Systolic BP, diastolic BP, and mean arterial pressure (MAP) at 0 wk (sham; B), 7 wk (C), and 15 wk (D) were measured using a noninvasive tail cuff system (CODA-2; n = 6–12). Scale bar = 50 µm. Data are expressed as means ± SD. ***P < 0.001 vs. sham; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; and ###P < 0.001.
