Figure 3.
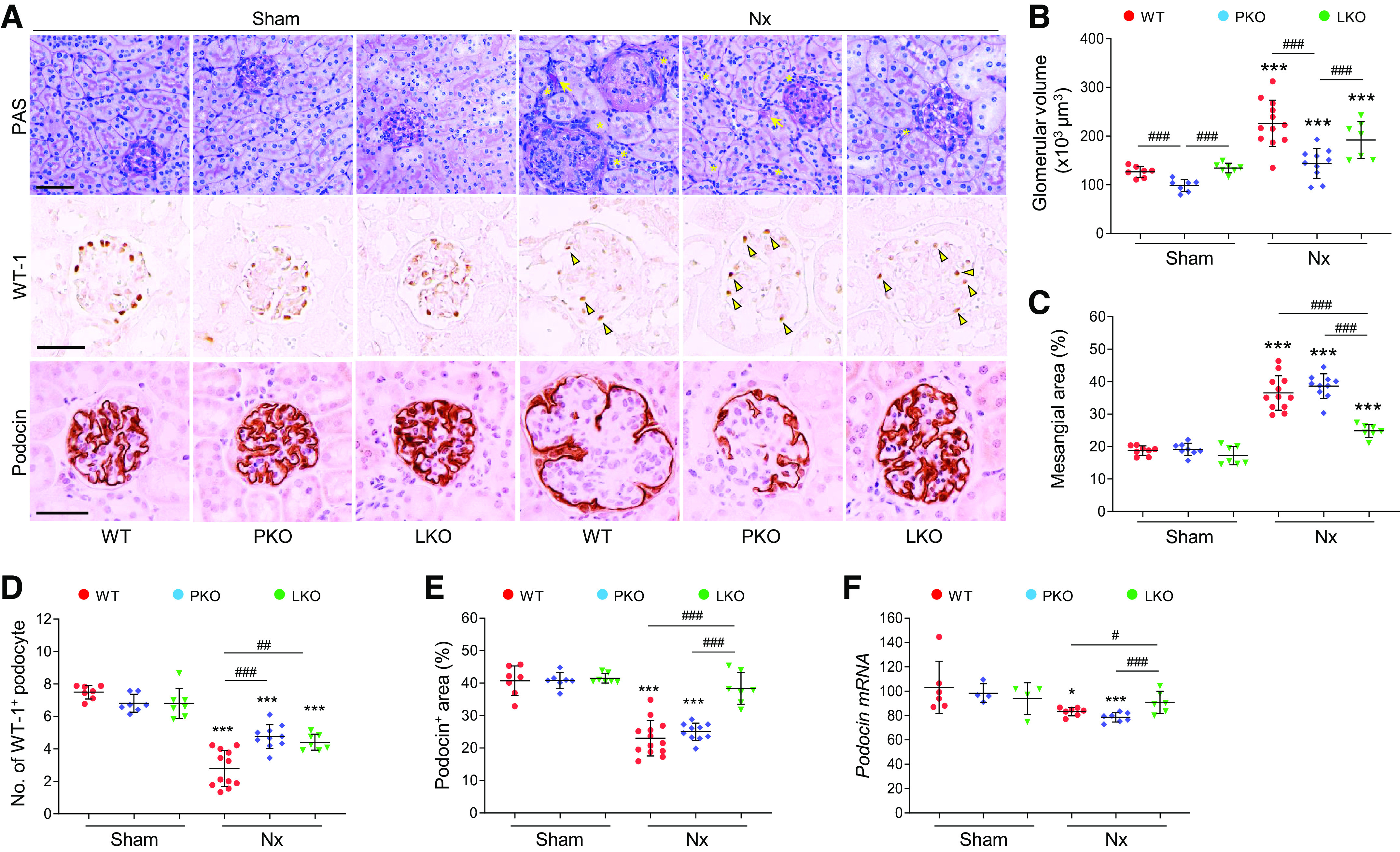
Role of tissue-specific angiotensinogen (AGT) in 5/6 nephrectomy (Nx)-induced glomerular injury. Kidney samples were collected at 16 wk post-Nx. A: paraffin-embedded kidney sections were used to carry out periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining and immunohistochemistry for evaluating the number of Wilms’ tumor-1 (WT1)-positive or podocin-positive podocytes. *Atrophied tubule. Arrows indicate tubular casts; arrowheads indicate WT1-positive podocytes. B: glomerular volume was calculated as described in materials and methods. C: mesangial area was expressed as a percentage of the mesangial-to-glomerular surface area. D and E: WT1-positive podocyte numbers and podocin-positive areas were counted from five randomly chosen fields or at least 30 glomeruli per kidney (n = 7–12). F: podocin mRNA levels were evaluated using quantitative RT-PCR and calculated using the formula described in MATERIALS AND METHODS (n = 4–7). Scale bars = 50 µm. Data are expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. the respective sham; ***P < 0.001 vs. the respective sham; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001. LKO, liver-specific AGT knockout; PKO, proximal tubule-specific AGT knockout; WT, wild type.
