Fig. 4. Respiratory tract (RT) retention of nicotine after use of E-cig and C-cig and its association with Cmax of brain nicotine accumulation following E-cig vapor inhalation.
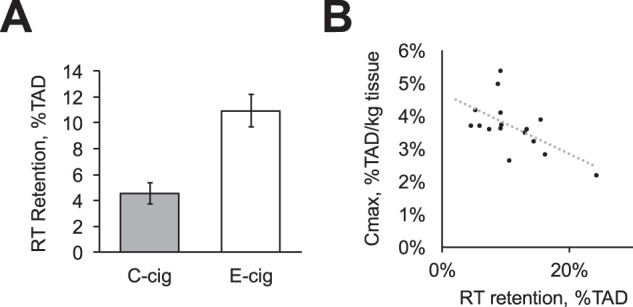
RT retention of nicotine after use of C-cig and E-cig (A) was assessed at 25 min after inhalation of a single puff from respective 11C-nicotine–containing product and expressed as percentage of total absorbed dose (TAD). Right panel (B) shows the association of brain nicotine accumulation (Cmax) with RT retention after using E-cig (rs = −0.59, p < 0.05 after correction for multiple testing). For other correlations, see Table 1.
