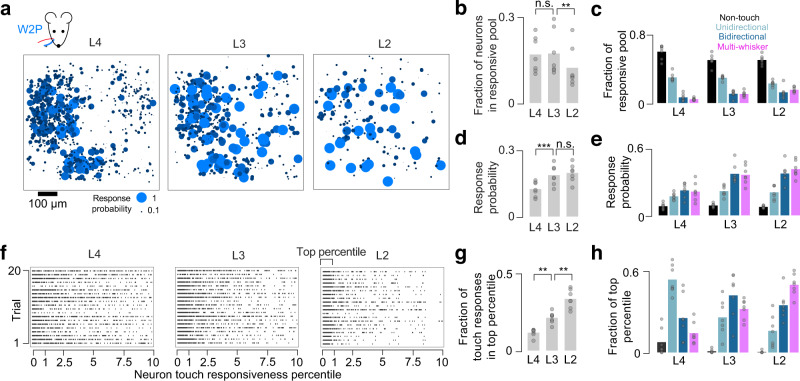
Fig. 4. Transition to sparser, more reliable responses from L4 to L2.
a Population response to strong W2P touches across layers. Ball size and color indicate response probability (Methods). All neurons for a layer are projected onto a single plane. b Fraction of neurons responding to strong W1P or W2P touches across layers (‘responsive pool’; Methods; mean, n = 7 mice). P-values indicated for paired t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s not significant. c Fractional composition of the responsive pool in each layer by touch neuron type. d Response probability across layers for neurons in this responsive pool (mean, n = 7 mice). e Response probability in each layer by touch neuron type. f Example W1P responses for 20 strong touch trials, one trial per row, one group of 20 trials per layer. Neurons are sorted left-to-right by responsiveness percentile. A dot indicates that a particular neuron responded on a given trial. g Fraction of touch-evoked calcium activity that originates from the top percentile of touch-responsive neurons (mean, n = 7 mice). h Neuron types comprising the most responsive percentile of neurons.