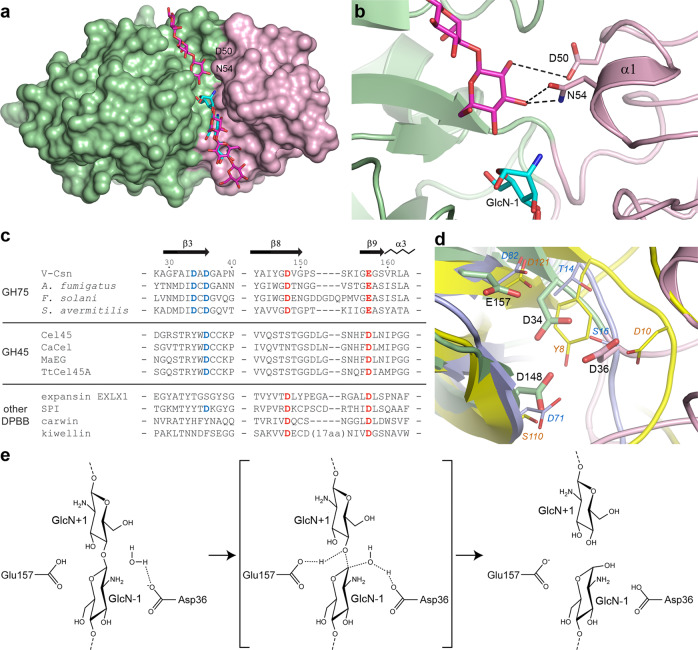
Fig. 6. Active site and reaction mechanism.
a Molecular surface representation of the E157Q-V-Csn mutant (green and pink domains) with cellohexaose (magenta sticks) modeled into the active site cleft based upon superposition of the chitohexaose-Cel45 complex (PDB code 4ENG). The three GlcN residues observed in the E157Q-VCsn complex are shown as cyan sticks. b The putative GlcN+1 recognition site in V-Csn based upon the superposition of the chitohexaose-Cel45 complex. c Partial structure-based sequence alignment of V-Csn with several enzymes containing DPBB domains. The alignment was determined from superpositions of the enzymes against V-Csn based upon their DPBB motifs. The four conserved acidic residues observed in the V-Csn active site are colored blue and red. Matching residues in the GH45 enzymes and other DPBB containing proteins are colored similarly when structurally equivalent. The sequences used are as follows: Cel45, endoglucanase V from Humicola isolens (Genbank P43316.1); CaCel, endoglucanase from Cryptopygus antarcticus (Genbank ACV50415.1); MaEG, endoglucanase from Melanocarpus albomyces (Genbank CAD56665.1); TtCel45A, endoglucanase from Thielavia terrestris (Genbank 1182607135); EXLX1, expansin from Bacillus subtilis (Genbank O34918); SPI, Steptomyces papain inhibitor from Streptomyces mobaraensis (Genbank WP_004951535.1); carwin from Carica papaya (Genbank 4JP6_A); kiwellin from Actinidia chinenesis (Genbank AGC39168.1). d Superposition of V-Csn (green and pink ribbons, green and pink sticks and black bold labels), Cel45 (yellow ribbon, thin yellow sticks and orange italic labels, PDB code 3ENG) and expansin EXLX1 (light blue ribbon, light blue sticks and cyan italic labels, PDB code 4FFT). The structures were superimposed by matching the DPBB motifs. e Schematic representation of the proposed glycoside bond cleavage reaction catalyzed by V-Csn. Glu157 is acting as the catalytic proton donor and Asp36 is acting as the catalytic base which accepts a proton from a water molecule.