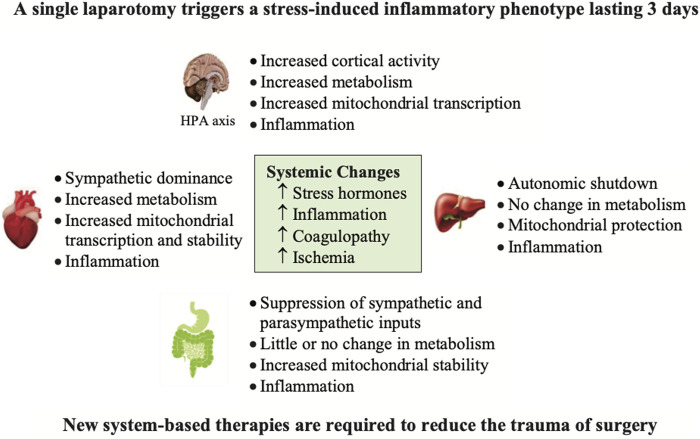
FIGURE 6.
The effect of a single transverse laparotomy on receptor gene expression in a number of tissues of the rat over a 3 day period (Dobson et al., 2021a). The trauma of surgery led to a proinflammatory phenotype involving neuroendocrine stress, cortical excitability, immune activation, lymphocytopenia, hypermetabolism and coagulopathy (Dobson et al., 2021a). Of special note was the profound hyperactivity of the brain and heart with no measurable changes in hemodynamics. In contrast, the liver and gut underwent downregulation of adrenergic and muscarinic receptor expression. This study illustrates the widespread effect of a single incision mimicking an abdominal trauma on altering brain and whole body homeostasis with no further surgery or manipulation (Dobson, 2020a; Dobson et al., 2021a). HPA, hypothalamo-pituitary axis.