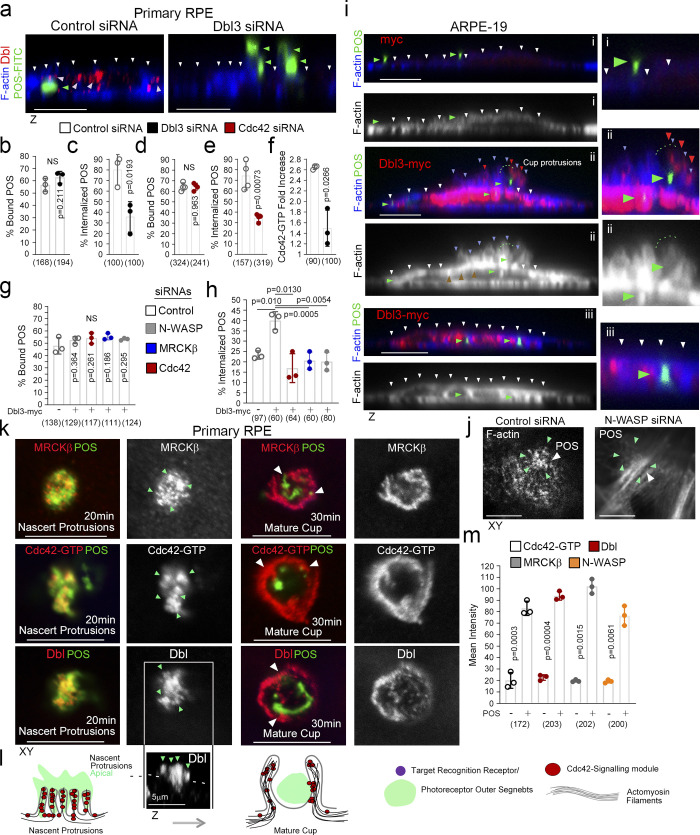
Figure 1.
Apical Cdc42 signaling drives cup formation and engulfment in the RPE. (a–e) siRNA-mediated knockdown of Dbl3 or Cdc42 in primary porcine RPE results in inhibition of phagocytosis. Note, in cells treated with Dbl3 siRNA, apical Dbl3 expression is lost. White arrowheads highlight apical F-actin cortex. Green arrowheads highlight the position of internalized or external bound POS. (f) siRNA-mediated knockdown of Dbl3 in primary porcine RPE inhibits Cdc42 activation. (g–i) Exogenous expression of Dbl3-myc in ARPE-19 cells stimulates increased POS-induced pseudopod and cup assembly, and phagocytosis via Cdc42, MRCKβ, and N-WASP signaling. White arrowheads highlight the apical F-actin cortex, green arrowheads highlight the position of POS, and red arrowheads Dbl3-myc. (j) N-WASP depletion in Dbl3-myc expressing ARPE-19 cells followed by 30 min of POS stimulation inhibits F-actin assembly at the vicinity of POS adhesion. White arrowheads indicate POS and green arrowheads F-actin. (k–m) POS-membrane contact rapidly induces membrane protrusions enriched in the Cdc42 GEF Dbl3, active Cdc42-GTP, and the Cdc42 effectors MRCKβ and N-WASP. Quantifications: means ±1SD of n = 3 independent experiments; indicated are the total number of cells analyzed and P values derived from t tests.