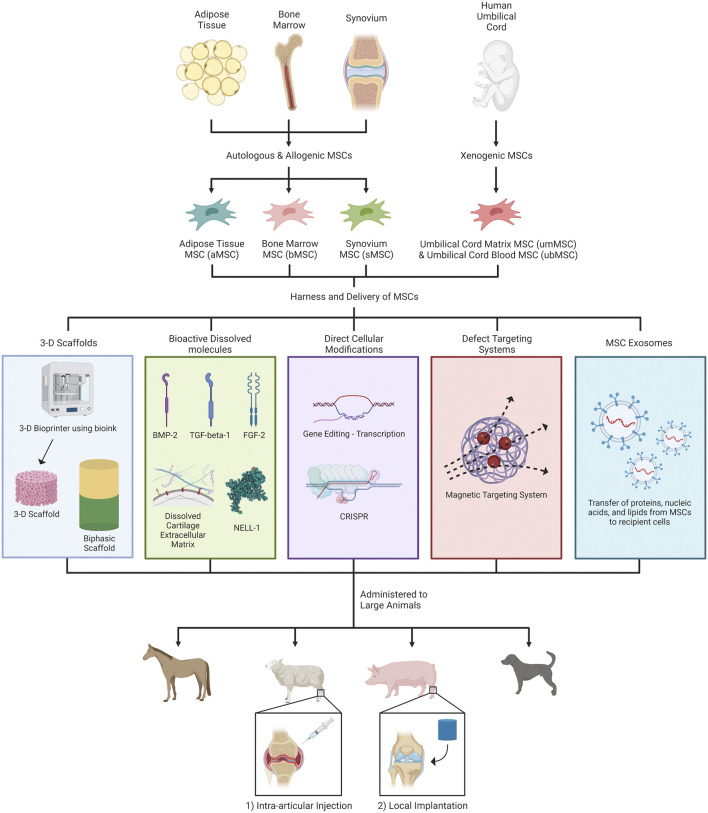
FIGURE 1.
MSC-harnessing strategies for articular cartilage regeneration in large animal models. Different types of MSCs—autologous, allogenic and xenogenic—were first obtained from adipose tissue (aMSC), bone marrow (bMSC), synovium (sMSC), and human umbilical cords (umMSC & ubMSC). Subsequently, MSCs were pretreated with and/or delivered through (1) 3-D scaffolds, (2) bioactive dissolved molecules, (3) direct cellular modifications, (4) defect targeting systems, and (5) cell-free MSC-derived exosomes, for enhancing cartilage regeneration and/or modulating inflammation. Currently, the two major routes of MSC administration in preclinical large animal studies are intra-articular injection and local implantation within chondral/osteochondral defects. Figure created with BioRender.com.