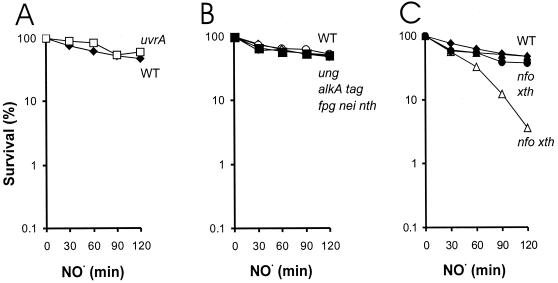
FIG. 1.
Relative NO⋅ sensitivity of E. coli strains carrying mutations in DNA excision repair pathways. Log-phase cells were exposed to 35 nmol of NO⋅/ml · min. (A) Survival of wild-type E. coli (black diamonds) and NER-deficient uvrA mutant cells (open squares) following NO⋅ exposure. (B) Survival following NO⋅ exposure of wild-type E. coli (black diamonds) and strains lacking expression of DNA glycosylases: alkA tag (open circles), fpg nei nth (open diamonds), and ung (black squares) strains. (C) Relative survival of wild-type E. coli (black diamonds), and strains lacking expression of AP endonucleases, xth (black circles), nfo (black triangles), and nfo xth (open triangles) strains, following NO⋅ exposure. For all panels, in cases where NO⋅ sensitivity is comparable to that of wild-type E. coli, the data presented are averages of at least two independent experiments. Data for wild-type AB1157 and the nfo xth strain are the averages of at least six independent experiments. There were no significant differences in sensitivity to NO⋅ among the wild-type strains that were used to create the mutant strains used in these studies (data not shown). WT, wild type.