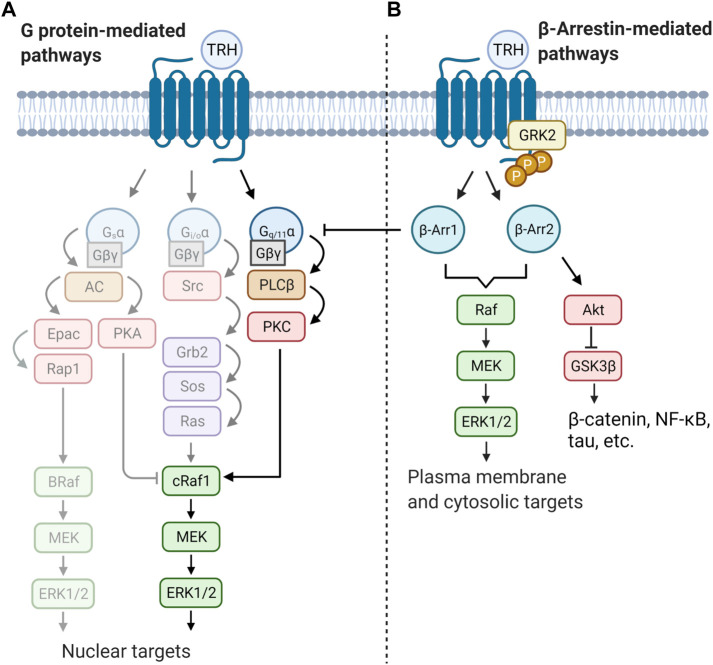
FIGURE 4.
Schematic illustration of two distinct modes of regulation of MAPK cascades triggered by TRH receptor. Activity of ERK is controlled by both G protein and/or β-arrestin-mediated pathways. Activation of receptor molecule by an agonist can lead to different signalling outputs depending on the cell type and signalling molecule supply. Basically, (A) TRH signals through the canonical Gq/11α–PLCβ–PKC pathway which can directly activate the first protein kinase from the MAPK cascade (cRaf1). Activated ERK then translocate to the cell nucleus. TRH may possibly activate other G proteins (lighter part) and further regulates gene transcription or cell cycle progression by phosphorylation of transcription factors. (B) β-Arrestin (β-Arr1 and β-Arr2) terminates G protein signaling by desensitization of TRH-R. Simultaneously it can function as scaffold activating another pool of ERK kinase which, afterwards, phosphorylates different substrates. The figure was created by BioRender.