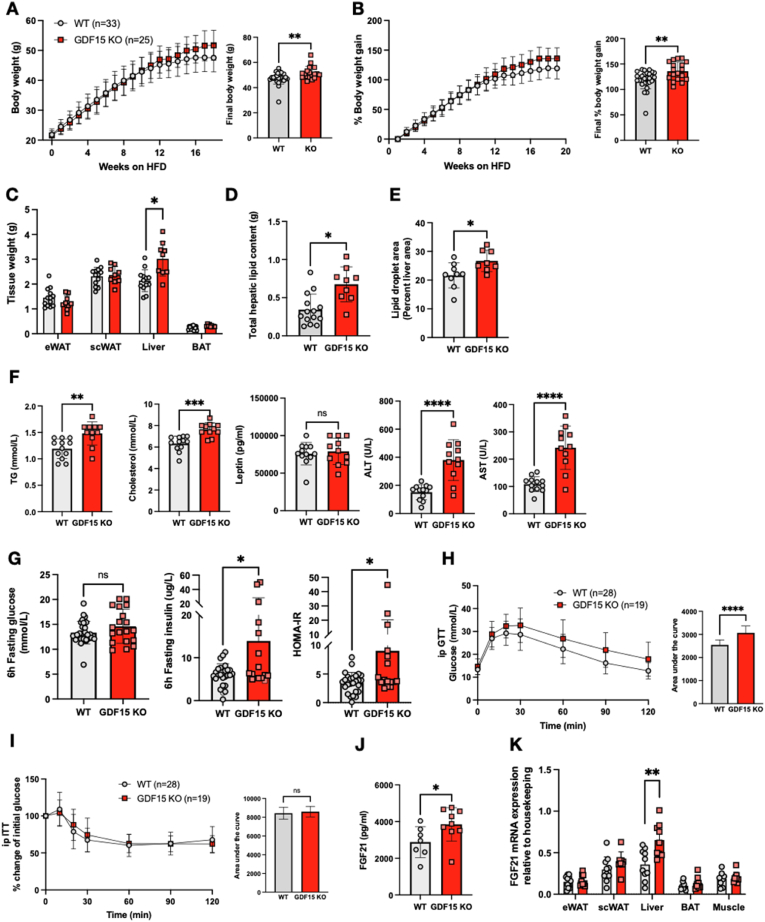
Figure 1.
Phenotypic characterization of GDF15 knockout mice on a highfat diet (HFD). (A and B) Body weight and percent body weight gain of wild type (WT) and GDF15 KO mice fed a 60% HFD; Inset, final body weight and percent body weight gain. (C) Weight of epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), subcutaneous white adipose tissue (scWAT), liver and brown adipose tissue (BAT), harvested at the end of the study, 25 weeks of HFD (n = 13,9). (D) Weight of total hepatic lipids in g; total lipid extracted from 25 mg tissue was normalized to total liver weight (n = 14,9). (E) Lipid droplet area (Percent liver area) determined from histological analyses of haematoxylin/eosin (H&E) stained liver sections (n = 9,8). (F) Plasma triglycerides (TG), cholesterol, leptin, alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) from random fed mice after 16 weeks of HFD-feeding (n = 12,11). (G) Blood glucose, plasma insulin and HOMA-IR levels from 6 h fasted mice, after 16 weeks of HFD feeding (n = 16–29). (H and I) Blood glucose levels during intraperitoneal (ip) glucose tolerance test (GTT) and percent change from initial blood glucose levels during insulin tolerance test (ITT) after 16 weeks of HFD feeding. Inset, area under the curve analysis of glucose over time. (J) Plasma FGF21 levels from random fed mice at 16 weeks of HFD feeding (n = 7,9). (K) FGF21 mRNA expression in tissues from WT and GDF15 KO mice after 25 weeks HFD feeding (n = 8–11). All data are means ± S.D ∗/∗∗/∗∗∗/∗∗∗∗ - p < 0.05/0.01/0.001/0.0001.