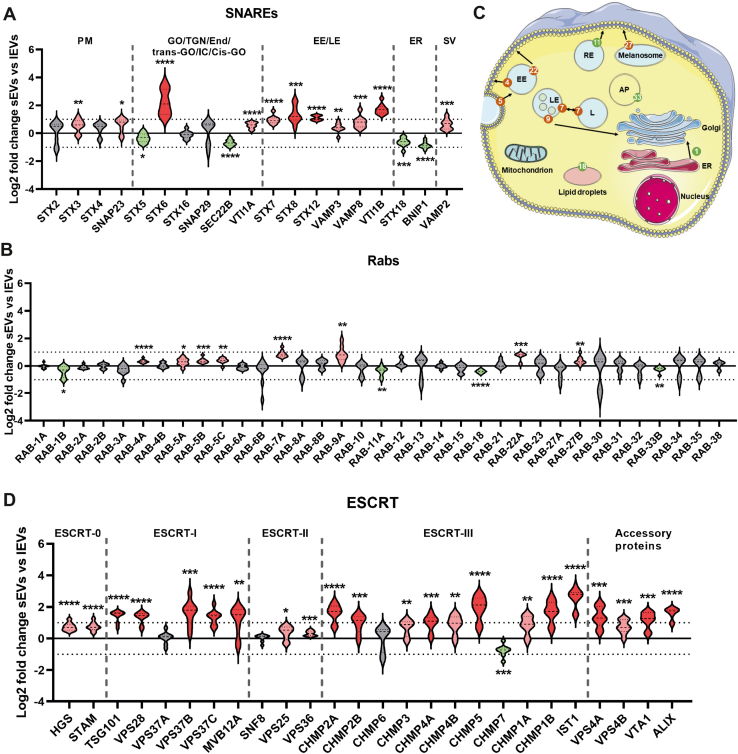
Fig. 6.
SNAREs and Rabs associated with endosomes and proteins from the ESCRT machinery are enriched in sEVs compared with lEVs.A, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics of all SNARE proteins detected in the dataset. Location of the SNAREs are according to Hong (57). B, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics of all Rab proteins detected in the dataset. C, the location of the enriched Rab proteins according to Hutagalung and Novick (90). Rabs enriched in sEVs and lEVs are labeled with red and green, respectively. D, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics for all proteins that are part of or associated with the ESCRT machinery. Light red, significant and fold change >1 (log2 = 0); dark red, significant and fold change >2 (log2 = 1) = enriched in sEVs. Light green, significant and fold change >−1 (log2 = 0); dark green, significant and fold change >−2 (log2 = −1) = enriched in lEVs. Gray, no significant enrichment in either sEVs or lEVs. Dotted lines on the y-axis indicate log2 fold change = 1 and −1 (corresponding to fold change 2 and −2). Data presented as violin plots. N = 9 (N = 3 for each of the three cell lines). AP, autophagosome; cisGO, cis-Golgi compartments; EE, early endosomes; End, endosomes; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GO, Golgi apparatus; IC, ER–Golgi intermediate compartments; L, lysosome; LE, late endosomes; lEV, large extracellular vesicle; PM, plasma membrane; RE, recycling endosomes; sEV, small extracellular vesicle; SV, synaptic vesicles; TGN, trans-Golgi network; trans-GO, trans-Golgi compartments.