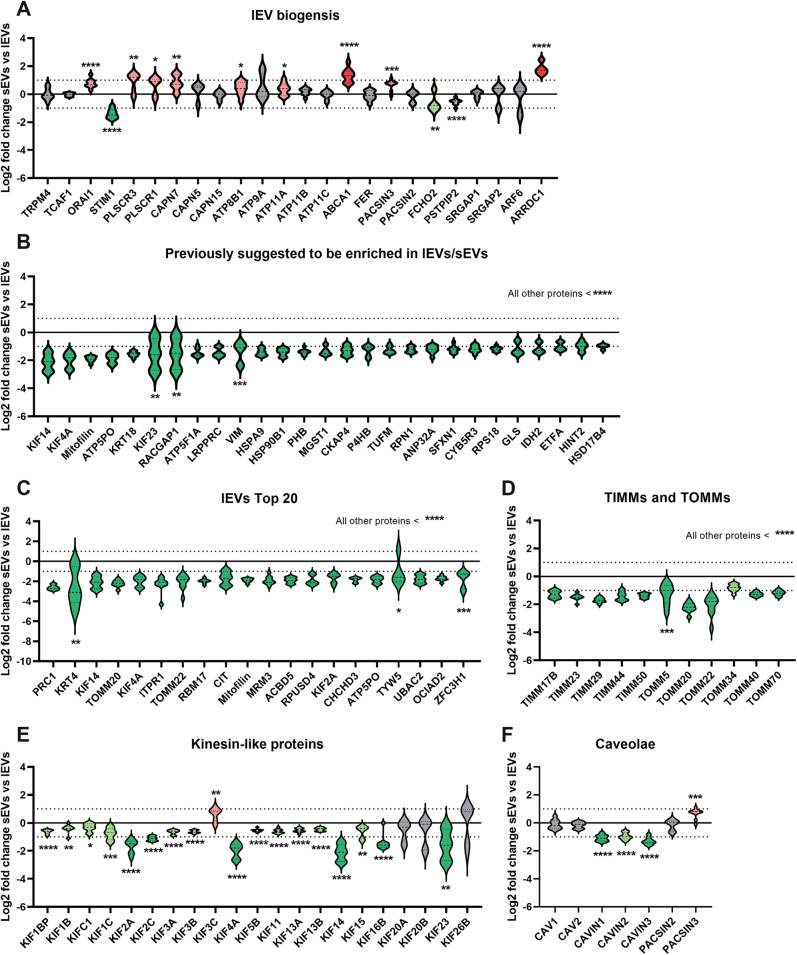
Fig. 7.
Mitochondrion- and cytokinesis-associated proteins are enriched in lEVs compared with sEVs.A, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics of proteins that have previously been suggested to be part of the biogenesis of the lEV subgroup, microvesicles/ectosomes (24, 25, 26). B, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics for proteins in our dataset with a log2 fold change below −1 that have previously been suggested to be enriched in the lEV subgroup, microvesicles/ectosomes compared with sEVs (26, 28, 29). C, the top 20 most enriched proteins in lEVs based on log2 fold change compared with sEVs. D and E, the log2 fold change determined with quantitative proteomics for all TIM and TOM proteins (D), all Kinesin-like proteins (E), and all Caveolae-associated proteins (F) quantified in the dataset. Light red, significant and fold change >1 (log2 = 0); dark red, significant and fold change >2 (log2 = 1) = enriched in sEVs. Light green, significant and fold change >−1 (log2 = 0); dark green, significant and fold change >−2 (log2 = −1) = enriched in lEVs. Gray, no significant enrichment in either sEVs or lEVs. Dotted lines on the y-axis indicate log2 fold change = 1 and −1 (corresponding to fold change 2 and −2). Data presented as violin plots. N = 9 (N = 3 for each of the three cell lines). lEV, large extracellular vesicle; sEV, small extracellular vesicle.