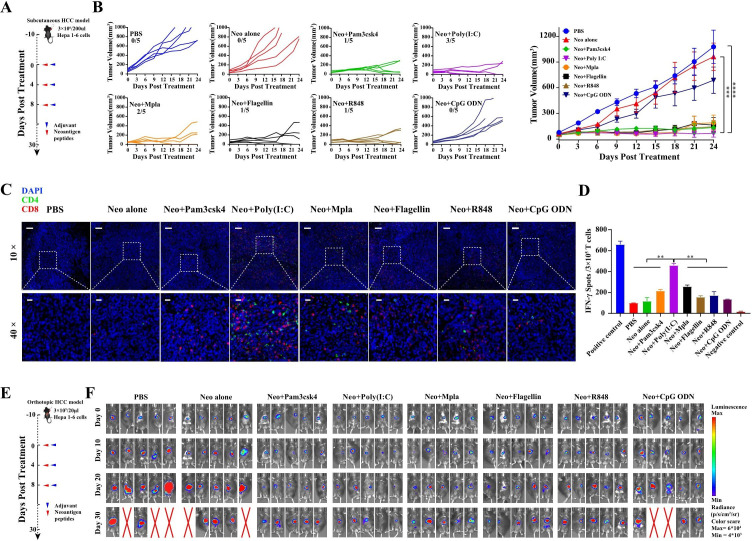
Figure 2.
Adjuvant optimization for neoantigen peptide vaccine NeoVAC preparation. (A) Schematic representation of the vaccination schedule for screening adjuvant in subcutaneous HCC model. (B) Tumor growth curves of each group (n=5) treated with neoantigen peptides pulsed with different Toll-like receptor agonists as adjuvant (Pam3cks4, Poly(I:C), Mpla, Flagellin, R848 and CpG-ODN). Results are shown as mean±SEM. (C) The representative immunofluorescence image of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell infiltration in tumor tissues at each treated group, Scare bars, 100 µm (10×), 40 µm (40×). (D) The histogram of ELISPOT assay showing neoantigen-specific reactivity of splenic T cells against the pool of seven neoantigen peptides. Results are shown as mean±SD. (E) Schematic representation of the vaccination schedule for screening adjuvant in orthotopic HCC model. (F) Tumor burden monitoring of each group (n=5) treated with neoantigen peptides pulsed with different adjuvant by bioluminescence imaging. Neo, neoantigen peptides. The statistical analysis was performed with analysis of variance analysis. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IFN, interferon; PBS, phosphate buffered saline.