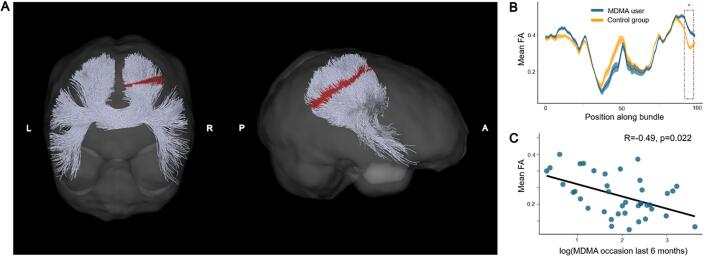
Fig. 2.
Increased levels of fractional anisotropy (FA) in the isthmus of the corpus callosum of chronic MDMA users compared to MDMA-naïve control participants. (A) Posterior coronal and right sagittal view of the isthmus. The isthmus is located between the body and splenium in the posterior part of the corpus callosum. Segments in the isthmus depicted in red indicate where MDMA users showed increased FA values after correction for multiple comparison (FWE < 5 %). (B) Mean FA values per segment and respective standard error along the isthmus are displayed separately for MDMA users (blue) and control participants (yellow). The area marked with a red dashed line corresponds to the significant area also colored red in (A). (C) Mean FA values of MDMA users in significant areas are negatively correlated with the number of MDMA use occasions during the six months prior to the study (Bonferroni corrected for multiple comparisons), suggesting that although MDMA users generally had elevated FA levels, this effect was most pronounced among weak-to-moderate users. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)