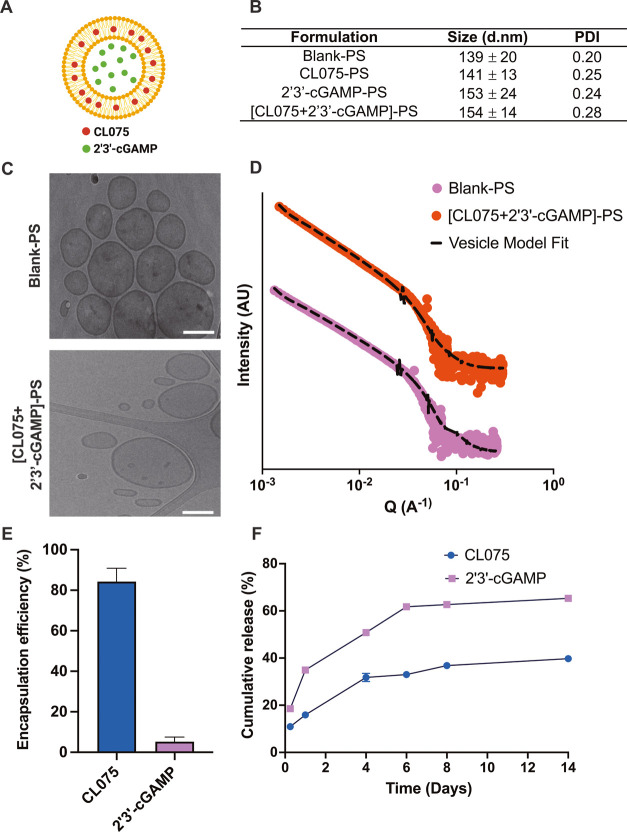
Figure 3.
cGAMP and CL075 encapsulation and characterization of adjuvant-loaded PEG-b-PPS polymersomes. (A) Schematic showing adjuvant-loaded-PEG-b-PPS PSs, with hydrophobic CL075 in the PS bilayer membrane and hydrophilic cGAMP in the aqueous core. (B) Dynamic light scattering analysis of blank and adjuvant-loaded PS formulations. Size (d nm) and polydispersity index (PDI) were reported as mean ± SD (n = 3). (C) Representative cryo-TEM images of blank-PS and dual adjuvant-loaded PS ((CL075 + cGAMP)-PS). TEM images were acquired at ×10 000 magnification (scale = 100 nm). (D) Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) profile and model fits for blank-PS and dual adjuvant-loaded PS ((CL075 + cGAMP)-PS). The scattering profile and vesicle model fit are represented as solid dots and dotted lines, respectively. (E) Encapsulation of CL075 and cGAMP in PS. The encapsulation of adjuvants was measured after purifying PS with size exclusion chromatography. Encapsulation efficiency (%) was reported as mean ± SD (n = 3). (F) In vitro release of CL075 and 2′3′-cGAMP from PS over 2 weeks (14 days). Release studies were performed in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) at 37 °C. Cumulative release (%) was reported as mean ± SD (n = 3).