Figure 6. Disruption of l-serine catabolism increases membrane permeability.
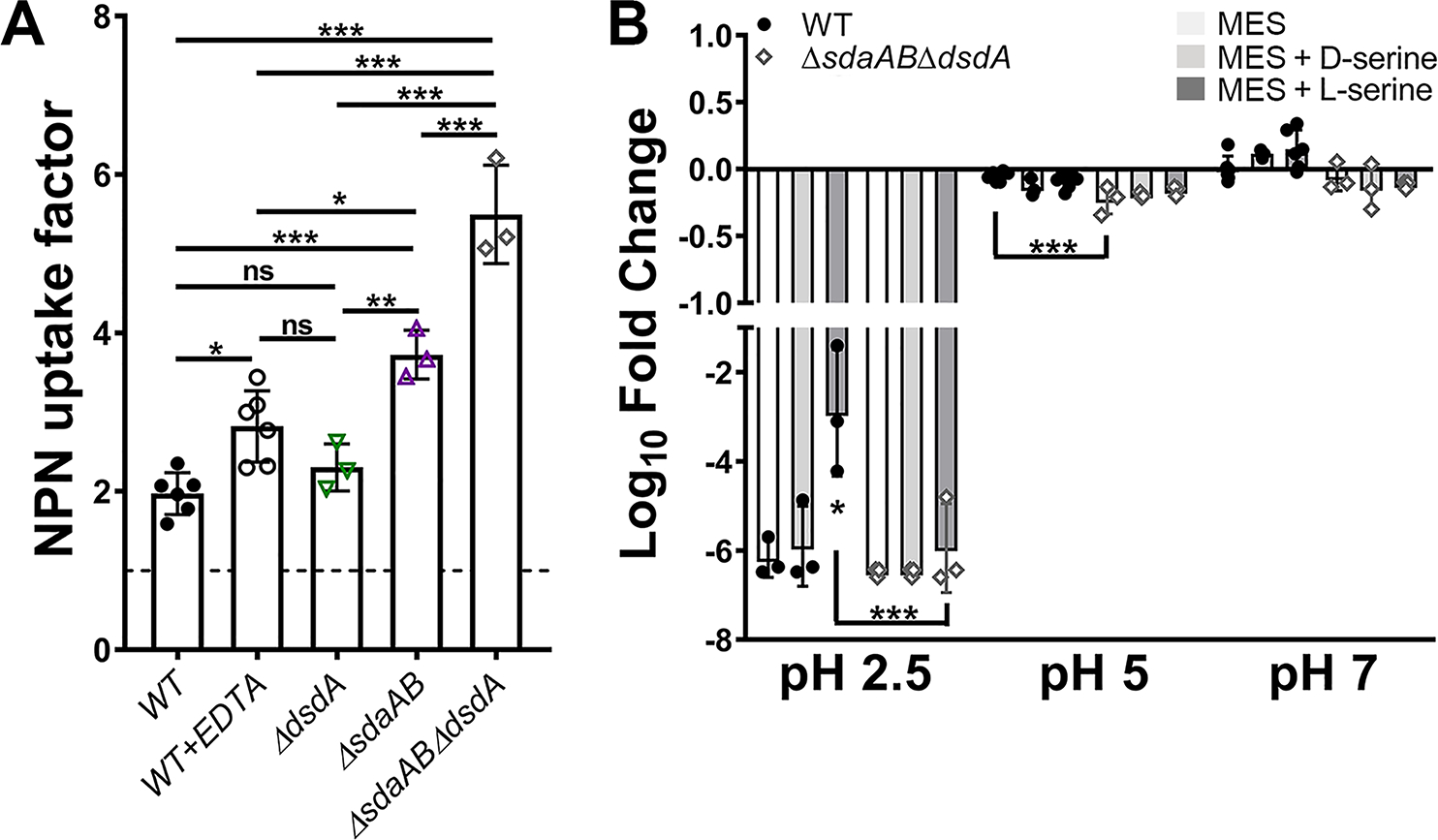
(A) Mid-log cultures of wild-type P. mirabilis and indicated mutants were adjusted to the same starting density in HEPES buffer and incubated with 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine (NPN), and an NPN uptake factor was calculated based on the fluorescence from background-subtracted samples and controls as described in the Methods section. Treatment with EDTA was included as a positive control for increased membrane permeability. Error bars represent mean ± SD from at least 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test for multiple comparison. ns=not significant. (B) Mid-log cultures of wild-type P. mirabilis and the sdaABdsdA triple mutant were adjusted to the same starting density in MES buffer at pH 2.5, 5, or 7 and incubated at 37°C for 1 hour prior to plating for determination of CFUs. Where indicated, MES was supplemented with 10 mM d-serine (light gray bars) or l-serine (dark gray bars). Error bars represent mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons.
