Figure 1.
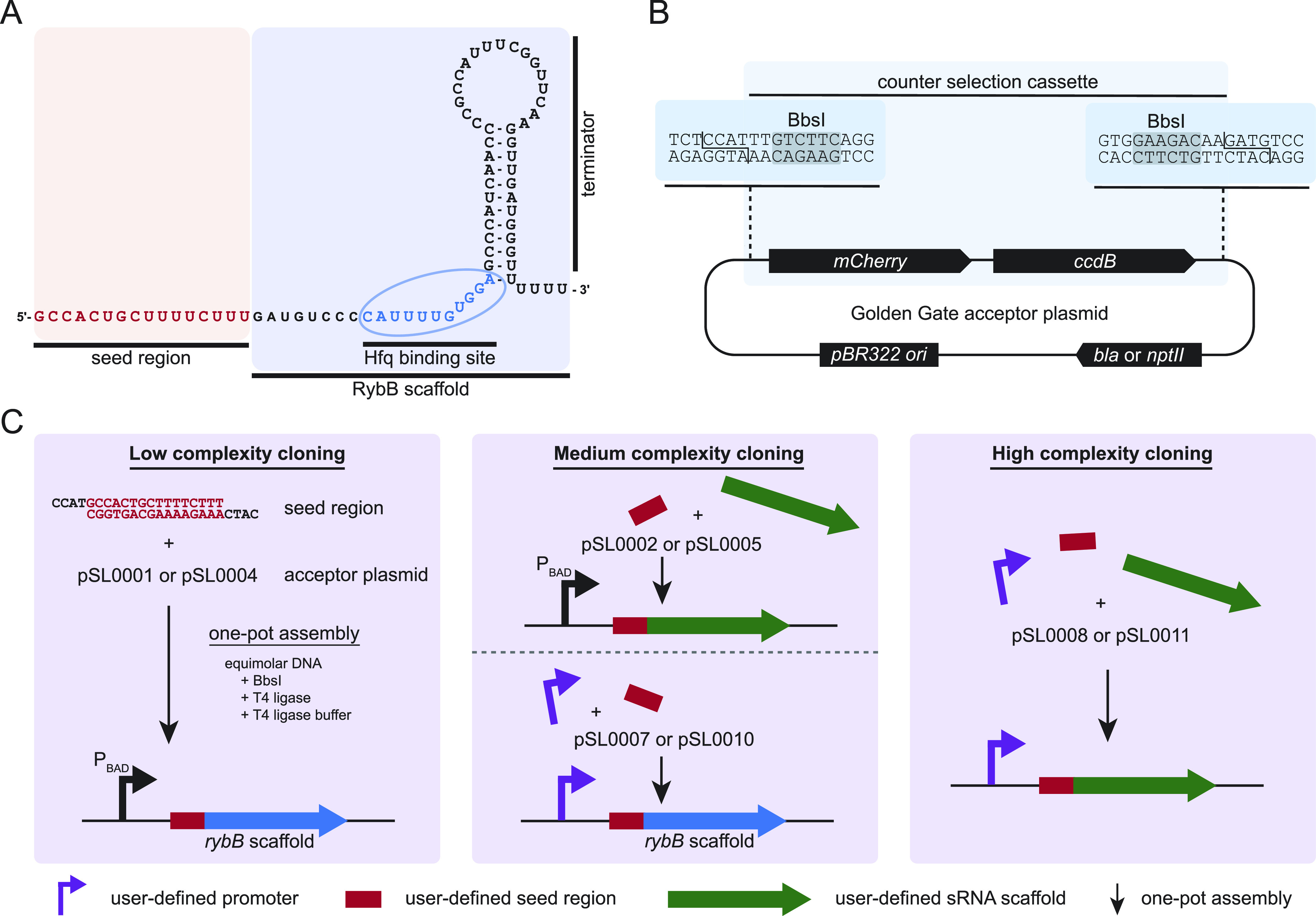
Structure and modules of the sRNA RybB and concept of the plasmid toolset. (A) Modules of wild-type RybB. The wild-type 16-nt seed region (red) consists of an imperfect match, multitargeting antisense sequence. The scaffold of RybB contains two elements, the Hfq binding site and the hairpin structure of the terminator. Structure according to RNAcentral.40 (B) Exemplary Golden Gate acceptor plasmid [pSL0001 (AmpR) or pSL0004 (KanR)] highlights the counter selection cassette containing the mCherry and ccdB gene flanked by BbsI recognition sites (highlighted in gray) to facilitate efficient type IIS-based cloning. The cloning relies on the type IIS recognition sites which are lost from the plasmid if the desired insert is ligated into the plasmid backbone, allowing a single-step, one-pot reaction.35 All constructed accepter vectors of the toolset contain the same counter selection cassette only differing in the sequence of the restriction sites and the properties of the plasmid backbone, allowing different complexities of cloning. (C) Different levels of cloning complexity that can be performed with the toolset. The low-complexity cloning allows the integration of any designed seed region into acceptor plasmids, resulting in a synthetic RybB TU under PBAD control (left panel). The medium-complexity cloning allows either the cloning of a designed seed region and an sRNA scaffold or the cloning of a promoter of choice and a seed region (center panel). The high-complexity cloning allows the user the combination of multiple fragments to create a synthetic sRNA TU. Visualized are the combination of the promoter, seed region, and sRNA scaffold, but more fragments could be assembled if the matching overhangs are designed (right panel).
