FIG 2.
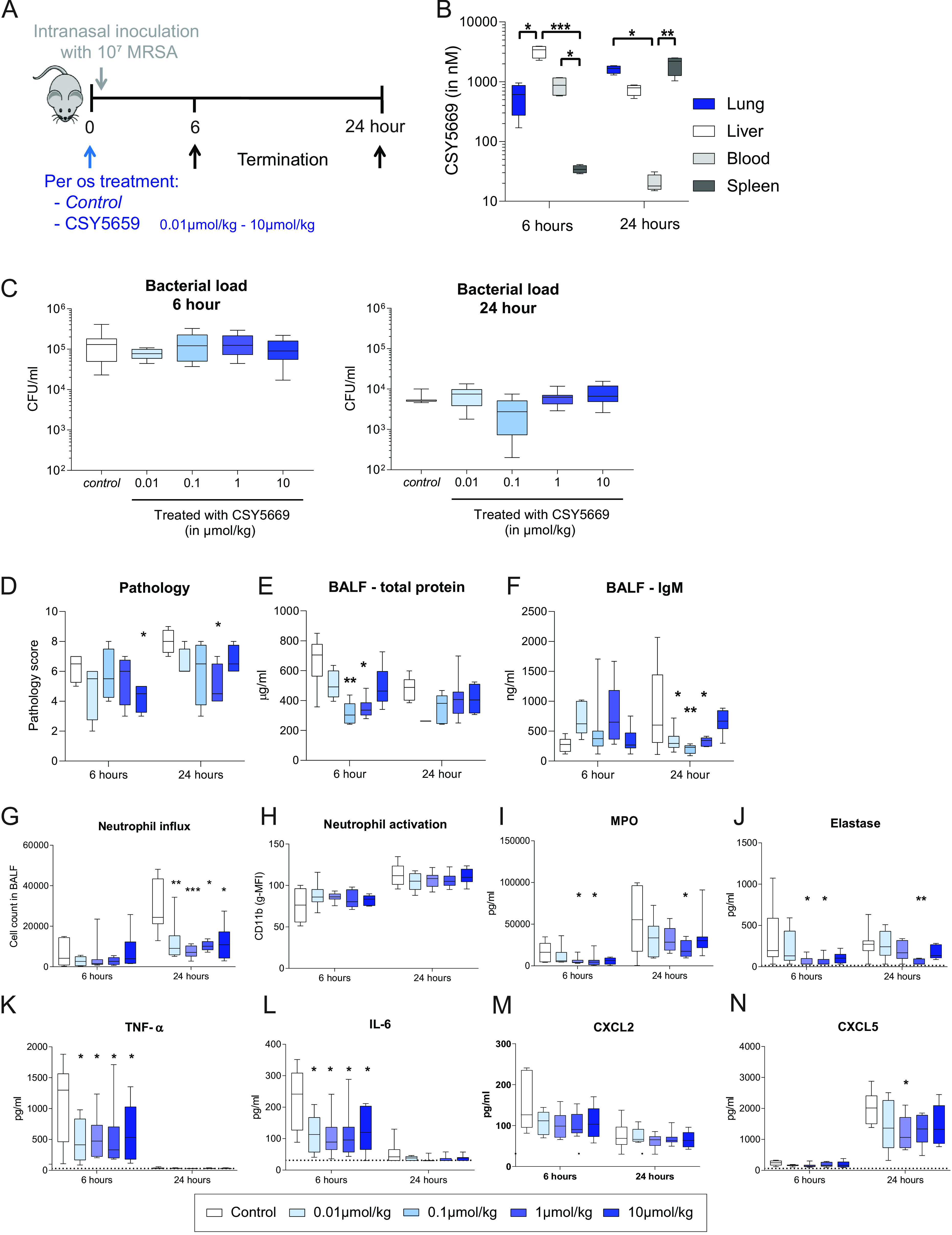
CSY5669 reduces lung inflammation and protein leakage during murine MRSA pneumonia. C57BL/6J mice were treated with 0 to 10 μmol/kg CSY5669 and were, directly thereafter, intranasally instilled with 107 CFU MRSA ([A], n = 8 per group). After 6 h or 24 h, the mice were sacrificed to determine the pharmacokinetics of CSY5669 ([B], n = 4), lung bacterial load ([C], n = 8) or lung damage ([D], n = 4) in extracted organs after homogenization (B and C) or formalin fixation (D). Parameters of vascular leakage (total protein and IgM) were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) obtained after one-sided BAL ([E, F], n = 4 to 8, except 24 h 0.01 mmol/kg CSY5669, for which n = 1). Cells were isolated from BALF using centrifugation, after which cells were phenotyped and enumerated using flow cytometry ([G, H], n = 6 to 8 per group; for the gating strategy used, see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Concentrations of myeloperoxidase ([I]; MPO), elastase (J), TNF-a (K), IL-6 (L), CXCL2 (M) and CXCL5 (N) were determined in supernatant BALF using ELISA. Data are presented as median 6 interquartile range (box) 6 range (whiskers). Differences from controls were tested for statistical significance using the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test (B to E). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
