FIG 3.
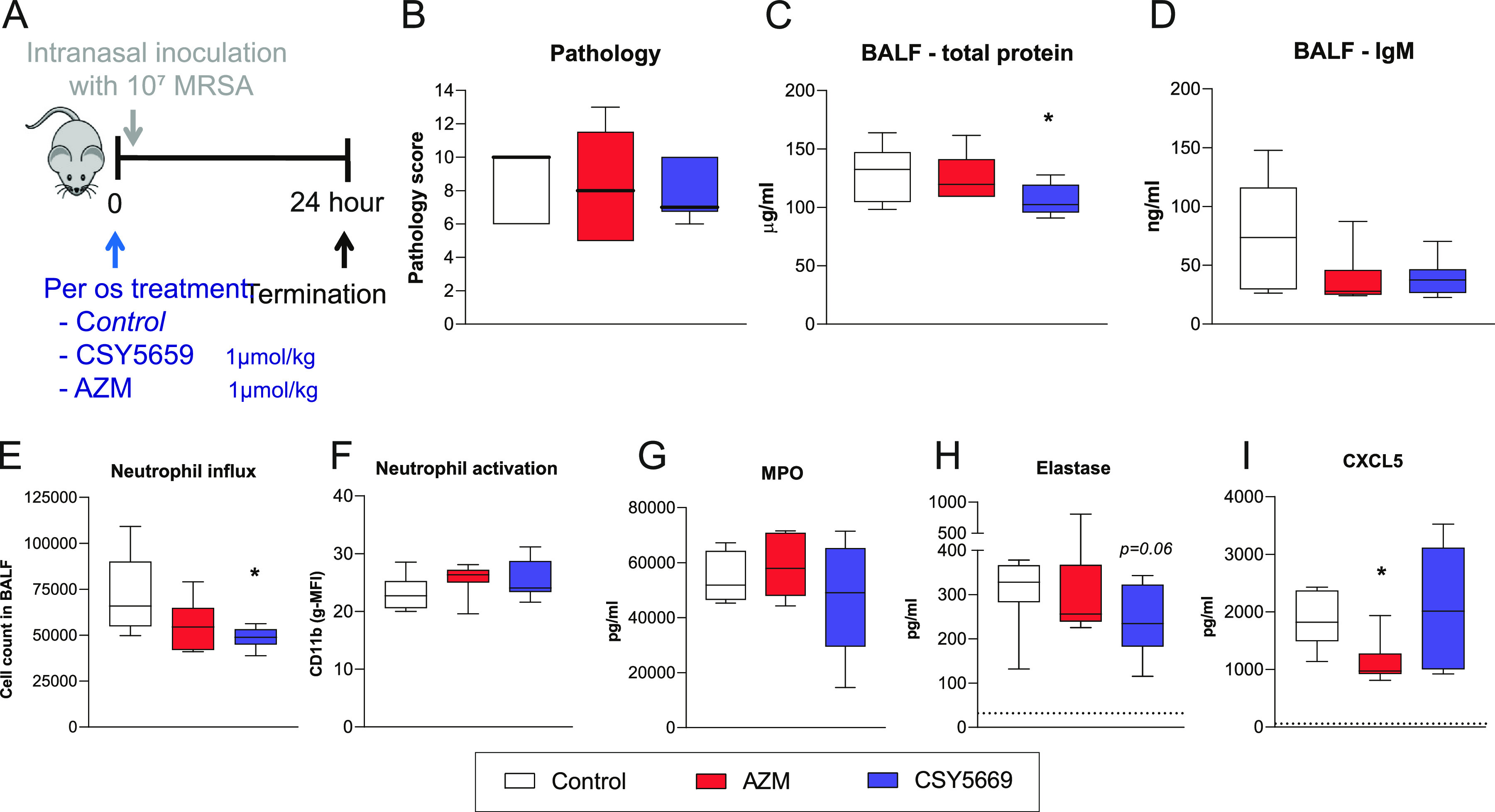
CSY5669 inhibits neutrophil recruitment and cytokine release during murine MRSA pneumonia more potently as AZM. MRSA pneumonia was induced in mice using the model presented in Fig. 3A, wherein BALF was obtained using one-sided BAL. Lung damage ([B], n = 4) was quantified in formalin fixed extracted organs. Parameters of vascular leakage (total protein and IgM) were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) obtained after one-sided BAL [C, D]. Cells were isolated from BALF using centrifugation, after which cells were phenotyped and enumerated using flow cytometry ([E, F]; for gating strategy, see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Concentrations of myeloperoxidase ([G]; MPO), elastase (H), and CXCL5 (I) were determined in supernatant BALF using ELISA. Dotted lines represent lower limits of detection. Data are presented as median ± interquartile range (box) ± range (whiskers). Differences from controls were tested for statistical significance using the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
