FIG 7.
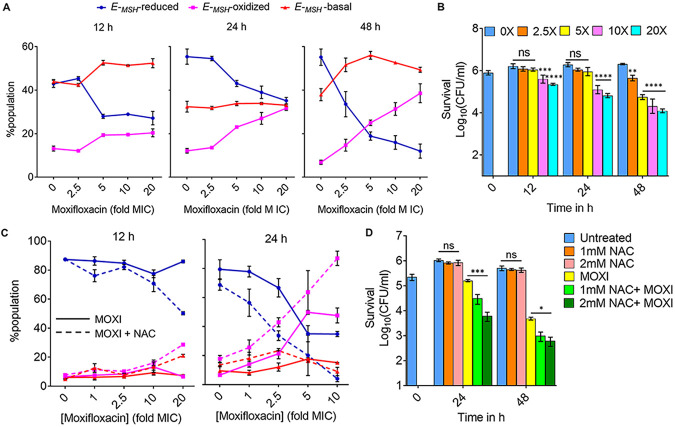
Moxifloxacin-induced oxidative shift in EMSH and killing of M. tuberculosis inside macrophages. THP-1 macrophages, infected with Mtb-roGFP2 (MOI = 1:10), were treated with moxifloxacin (MOXI; 1× MIC = 0.5 μM) immediately after infection and incubated for the indicated times. (A) Approximately 10,000 infected macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry to quantify changes in the EMSH of M. tuberculosis subpopulations. (B) Bacterial survival kinetics after MOXI treatment of THP-1 macrophages infected with Mtb-roGFP2 (CFU determination). (C) Mtb-roGFP2-infected THP-1 macrophages were treated with MOXI at the indicated concentrations in the presence or absence of NAC (1 mM) immediately after infection and incubated for the indicated times; analysis was as for panel A. (D) THP1 macrophages, infected by Mtb-roGFP2, were treated with NAC (1 mM or 2 mM), MOXI (10 μM), or the combination of NAC plus MOXI at those concentrations. After the indicated incubation times, the bacterial load in the macrophages was determined by plating on drug-free agar. P was determined by two-tailed Student's t test compared to MOXI-alone treatment at each time point. Statistical considerations were as for Fig. 1.