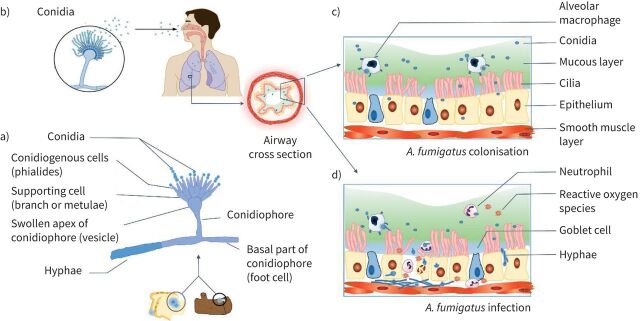
FIGURE 1.
Aspergillus fumigatus from transmission to colonisation or infection. a) Microscopic morphology of Aspergillus which can grow on dead wood or starchy foods [29]. b) Inhalation of conidia into airways. Panel b) is reproduced and modified from [29] with permission. c) Colonisation of A. fumigatus in the airways in people with cystic fibrosis, where due to impaired mucociliary clearance of the thick mucus layer, the inhaled conidia are not eliminated. d) A. fumigatus infection in which germination of conidia leads to hyphal growth and tissue invasion triggering neutrophil recruitment and the release of reactive oxygen species which mediate a multitude of inflammatory pathways causing damage to the airways.