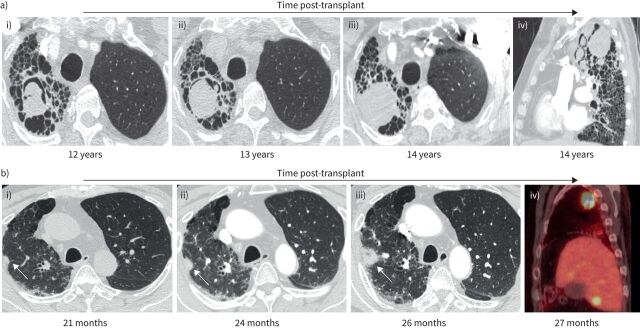
FIGURE 2.
Examples of post-transplant complications in the native fibrotic lung after single lung transplantation (SLTx). a) Images from a 57-year-old male 12 years after left SLTx for familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; i) demonstrates a mycetoma in the native right upper lobe on axial computed tomography images. Bronchoalveolar lavage cultures from the (native) right upper lobe as well as from the (allograft) left upper lobe grew Aspergillus fumigatus. He was treated with prolonged voriconazole, but surveillance imaging showed increasing size of the mycetoma at ii) 13 and iii) 14 years post-transplant, with iv) sagittal imaging also demonstrating several new, smaller mycetomas. b) Images from a 62-year-old male 21 months after left SLTx for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. On axial computed tomography, i) demonstrates a small nodule versus focus of scarring superimposed upon underlying fibrosis in the native lung (arrow). ii, iii) Surveillance imaging demonstrated evolution into a clear nodule which increased in size over 5 months (arrows). iv) Positron emission tomography (sagittal image) confirmed a hypermetabolic right upper lobe nodule, along with multiple hypermetabolic lesions in the liver consistent with metastases. Percutaneous biopsy of the lung nodule confirmed adenocarcinoma. The patient died at 29 months post-transplant due to complications from brain metastases.