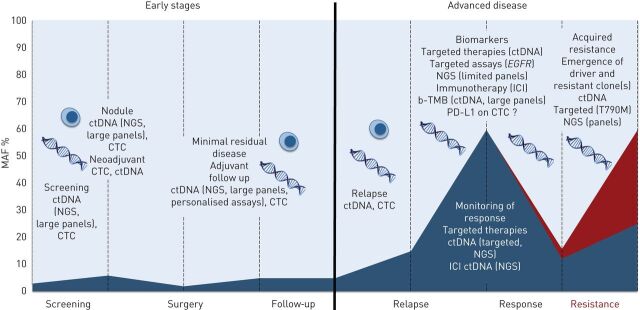
FIGURE 3.
Potential applications of liquid biopsy in nonsmall cell lung cancer throughout treatment. In early stage disease, screening requires plasma next-generation sequencing (NGS) using large panels, with both high sensitivity (limited by low tumour shed) and perfect specificity, or highly specific circulating tumour cell (CTC) detection platforms. To discriminate benign from malignant nodules, plasma NGS could be useful and avoid invasive biopsies. Circulating tumour (ct)DNA or CTCs burden before surgery have the potential to help guide neoadjuvant therapy, while minimal residual disease detection after surgery (large or patient-specific NGS panels) may guide adjuvant therapy. In advanced stage disease, plasma genotyping is well established in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) setting, and NGS platforms allow for a wider genotyping at both diagnosis (including other oncogenic drivers detection and blood tumour mutation burden (b-TMB) estimation) and resistance. MAF: mutant allele frequency; ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; PD-L1: programmed-death ligand 1.