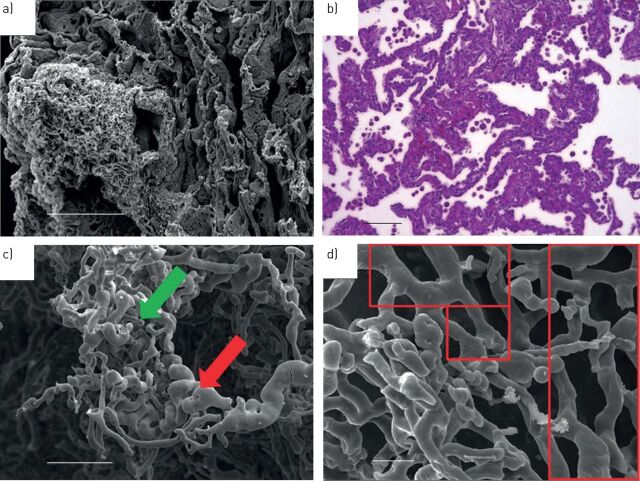
FIGURE 5.
Structure and architecture of pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD) and pulmonary capillary haemangiomatosis (PCH). Prominent and back-to-back proliferation of capillaries in an area with PCH a) by scanning electron microscope and b) in a complementary haematoxylin–eosin stain. c, d) Scanning electron microscope following microvascular corrosion casting of affected lung tissue reveals capillary neo-formation by sprouting (green arrow in c) and intussusceptive vascular pillars (red arrow in c) next to non-remodelled pulmonary capillaries (red frames in d). Scale bars: a) 200 µm; b) 100 µm; c) 100 µm; d) 20 µm. Reproduced from [67] with permission.