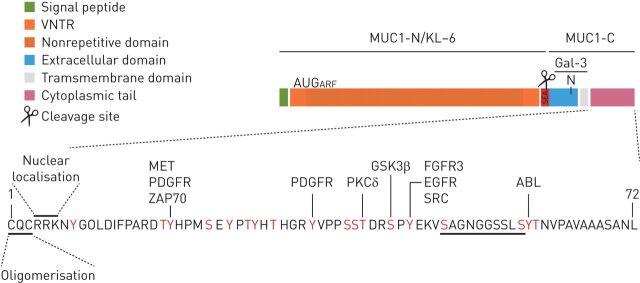
FIGURE 1.
Structure of mucin 1 (MUC-1). MUC1 protein comprises an N-terminal subunit (also called KL-6) constituted by a signal peptide, a VNTR domain composed of 25–125 repeats of 20 amino acids and the SEA domain. MUC1-C-terminal subunit has a 58-amino acid extracellular domain, a single-pass 28-amino acid transmembrane domain and a 72-amino acid CT. The MUC1 extracellular domain can be shed into the lumen by auto-proteolytic cleavage in the SEA domain or by the action of metalloproteinase 14 in the region following the SEA domain. The MUC1-C extracellular domain is glycosylated on Asn-36 and then serves as a binding site for the profibrotic galectin 3 ligand. MUC1-CT serves as a substrate for phosphorylation (18 documented and putative tyrosine and serine/threonine potential phosphorylation sites) in response to activation of several growth factor receptors and/or kinases. The CQC motif is necessary for MUC1-C oligomerisation and the RRK motif is necessary for MUC1-C binding to importin β and targeting to the nucleus. β-catenin-binding site is also localised to MUC1-CT. An AUG codon downstream to the MUC1 initiation codon has been described to initiate an ARF thereby generating a novel protein, MUC1-ARF. ABL: tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1; ARF: alternate reading frame; CT: cytoplasmic tail; FGFR: fibroblast growth factor receptor; Gal-3: galectin-3; GSK3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; KL-6: Krebs von den Lungen-6; MET: tyrosine-protein kinase Met; MUC1-C: mucin 1 C-terminal; MUC1-N: mucin 1 N-terminal; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PKCδ: delta isoform of protein kinase C; SEA: sperm protein, enterokinase and agrin; VNTR: variable number tandem repeat; ZAP70: zeta chain of T-cell receptor associated protein kinase 70.