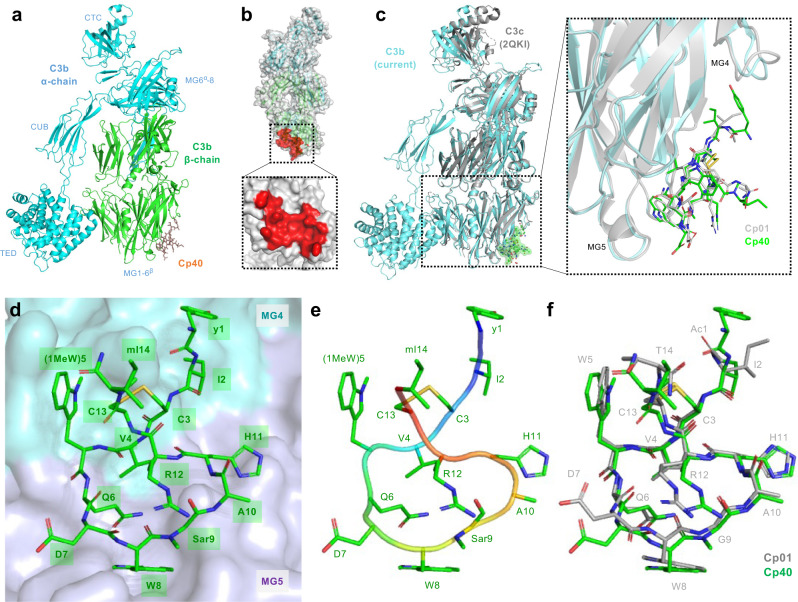
Fig. 2. Crystal structure of Cp40-C3b complex and comparison with Cp01-C3c structure.
a Cp40-C3b structure solved at 2.0-Å resolution showing a single molecule of Cp40 (stick representation) binding to the β-chain of C3b (green, cartoon representation; the α-chain is shown in cyan). b Cp40 binding site at the MG core of C3b highlighted in red. c Superimposition of the current Cp40-C3b structure (green/cyan) with the previous Cp01-C3c structure (grey). The dotted box shows an enlarged view of the compstatin binding region at the interface of the MG4 and MG5 domains of C3b/C3c. The two compstatin analogs are shown as sticks. d–f Structure of Cp40 in its target-bound conformation. d Cp40 is bound as cyclic 14-amino-acid peptide (green stick representation) engaging in intermolecular contacts with the MG4 (cyan) and MG5 (purple) domains of C3b. e Backbone trace (main chain as cartoon, side chain as sticks) revealing a twisted, O-shaped bound conformation of the disulfide-bridged peptide f Superimposition of Cp01 (grey; from C3c-Cp01 complex) and Cp40 (green; from C3b-Cp40 complex) showing an overall structural similarity with deviations primarily found in side chains not engaging in tight intermolecular interactions. CTC C-terminal complement domain, CUB complement C1r/C1s, Uegf Bmp1 domain, MG macroglobulin domain, TED thioester-containing domain.