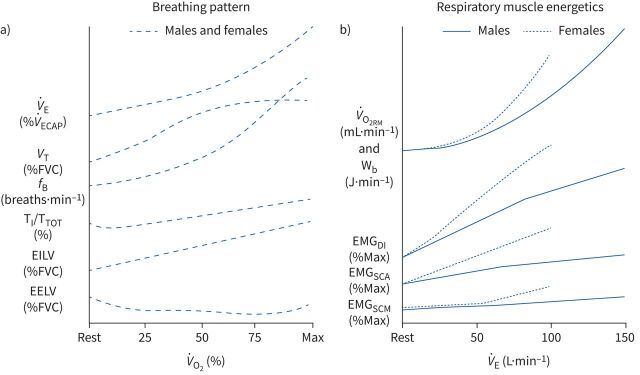
FIGURE 1.
Sex differences and similarities in breathing pattern and respiratory muscle energetic responses to incremental exercise. The x-axes represent progressive increases in relative oxygen uptake (panel a) and absolute minute ventilation (panel b) from rest to maximal exercise intensity. The y-axes are unitless and are intended to illustrate the pattern of change; however, units for each variable are provide in parentheses. In panel b, the curves for each sex are extrapolated to the average maximal exercise minute ventilation in healthy, young adults of average cardiorespiratory fitness. EELV: end-expiratory lung volume; EILV: end-inspiratory lung volume; EMGDI: electromyographical activity of the diaphragm; EMGSCA: electromyographical activity of the scalene; EMGSCM: electromyographical activity of the sternocleidomastoid; fB: breathing frequency; TI/TTOT: inspiratory duty cycle; V̇E: minute ventilation; V̇O2RM: oxygen uptake of the respiratory muscles; VT: tidal volume; Wb: work of breathing.