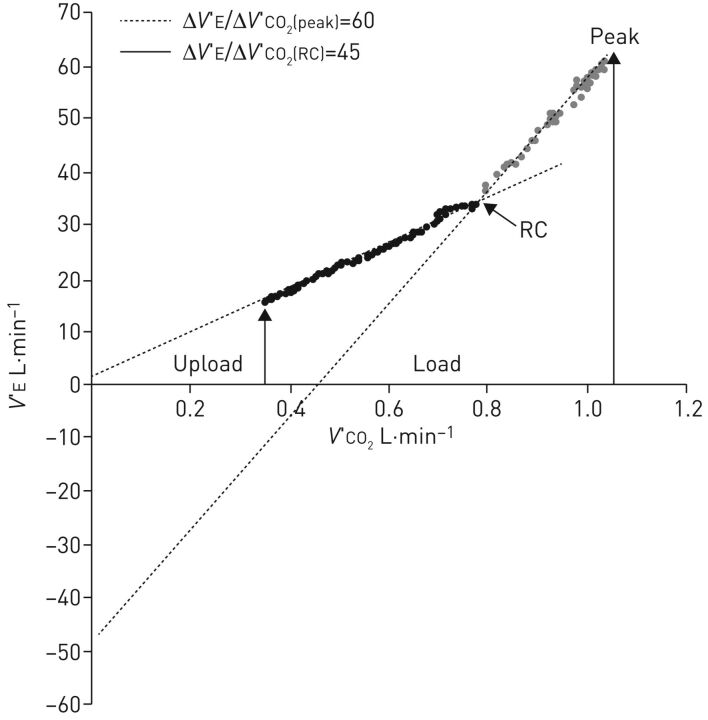
FIGURE 2.
The minute ventilation (V′E)/carbon dioxide production (V′CO2) relationship slope in a patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension and preserved physiological behaviour of the V′E/V′CO2 relationship during exercise. In the first part of exercise, the V′E/V′CO2 slope is high and the V′E-axis intercept is close to zero. This means that dead space ventilation progressively increases during exercise. After the end of isocapnic buffering, i.e. at the respiratory compensation (RC) point, the slope becomes steeper and the V′E-axis intercept becomes severely negative showing that dead space ventilation severely increases toward the end of exercise. Reproduced from [32] with permission.