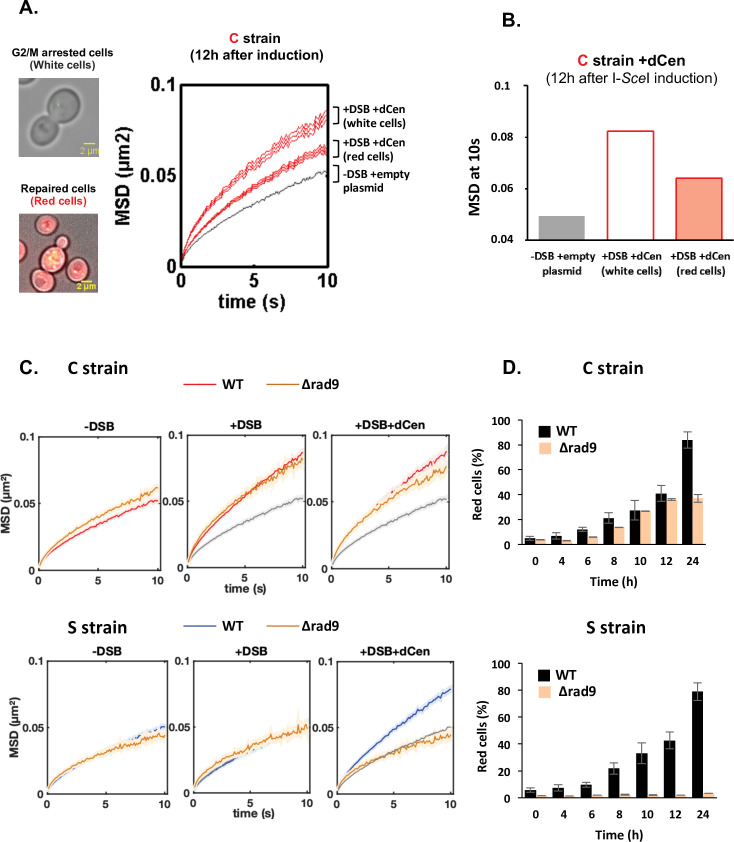
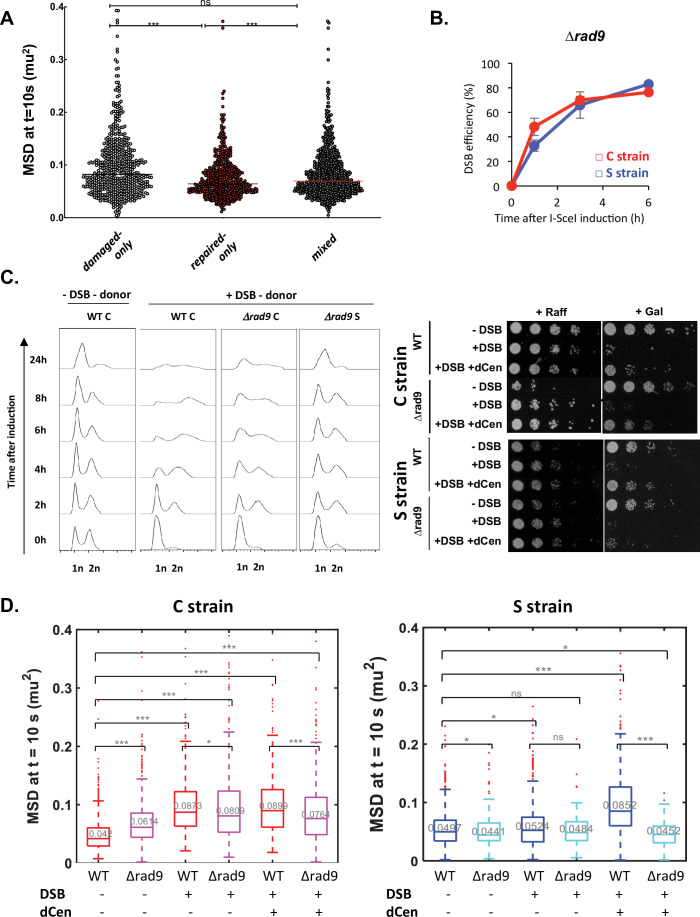
Figure 3. Proximal mobility is Rad9 independent.
(A) Non-repaired cells (white cells, n=584) show increased global mobility, while repaired cells (red cells, n=519) recover normal global mobility. Mean squared displacements (MSDs) of the visualization of the locus on chromosome V (V-Vis) locus in strain C as a function of time, calculated as in Figure 2A. The gray and red curves correspond respectively to strain C in the presence of the donor dCen plasmid after 12 hr in galactose medium with a plasmid not expressing I-SceI (-DSB) and expressing I-SceI (+DSB). MSDs are calculated after color visual cell sorting. Red MSD full curve corresponds to cycling red cells, red empty curve corresponds to white G2/M arrested cells. Examples of white, G2/M arrested and red, cycling cells are shown. Bar scale, 2 µm. Seven independent experiments were done. (B) Box plots of MSDs at 10 s of undamaged, white and red cells 12 hr after I-SceI induction. The color code corresponds to that used in (A). (C) MSDs in strains C and S in wild-type (WT) and Δrad9 mutant. MSDs are calculated as in Figure 2 upon 6 hr of double-strand break (DSB) induction with empty plasmid or with dCen plasmid (+DSB: n=380 [C strain], n=103 [S strain], and +DSB+dCen: n=452 [C strain], n=98 [S strain], respectively). Controls without DSB are also shown (-DSB: n=590 [C strain], n=176 [S strain]). (D) Homologous recombination (HR) kinetics upon induction of I-SceI in the presence of dCen in WT (black) and Δrad9 (orange) C or S strains were measured by FACS as in Figure 1F. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments.