Figure 2: Ifi204 modulation of periodontal bone loss originates from a non-marrow source of cells.
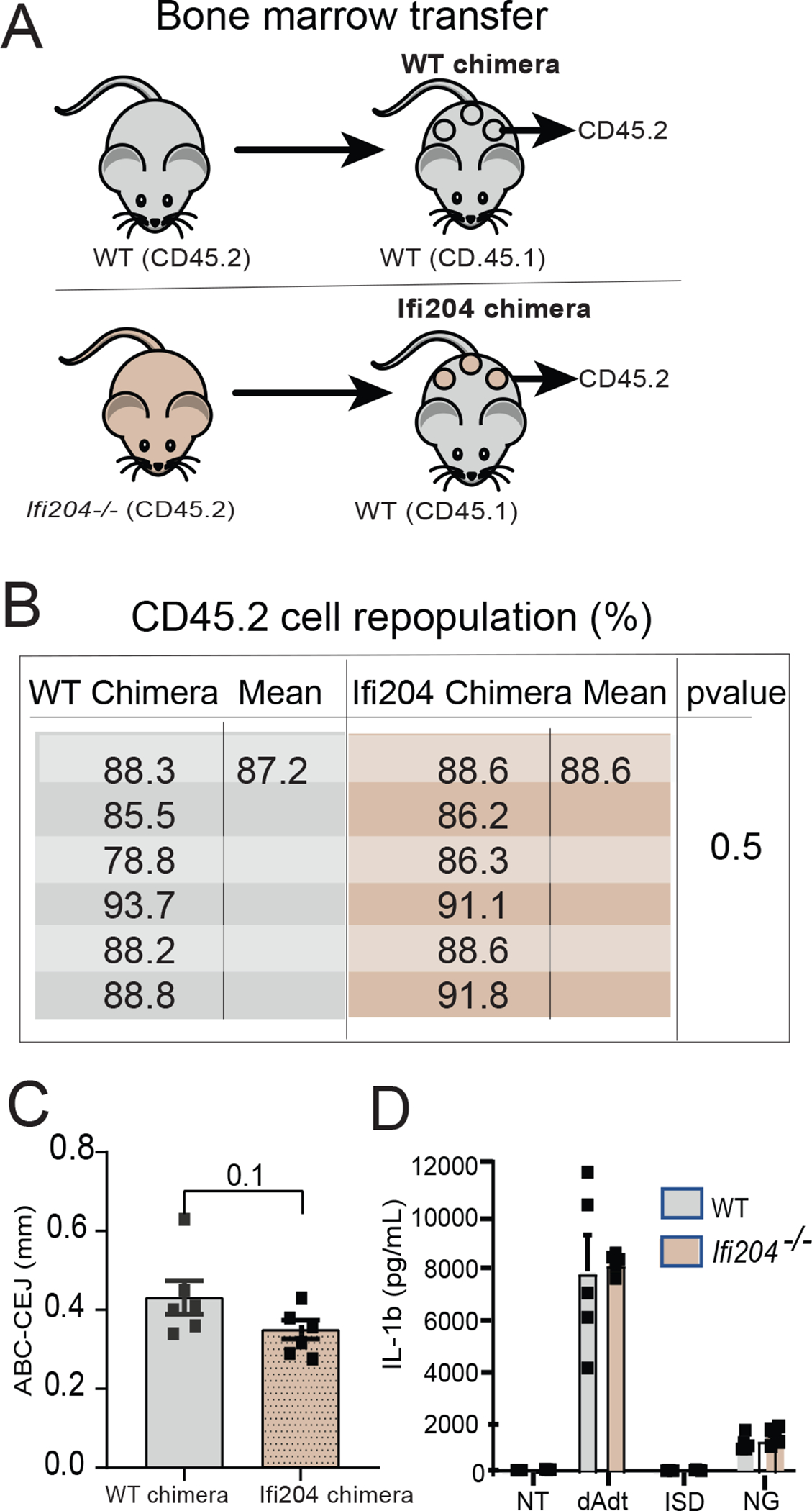
Chimeric mice were created to determine the cellular source responsible for the enhanced bone loss in the absence of Ifi204. A) Schematic representation of the bone marrow transfer (BMT) experiment. WT mice (CD45.1) were exposed to whole-body radiation (8 Gy) to deplete the hematopoietic-progenitor compartment. Irradiated recipient mice were then reconstituted with bone marrow from WT mice or Ifi204−/− (CD45.2). B) Flow cytometry analysis of CD45.2 reconstituted cells in WT chimera and Ifi204 chimera (n=6/group). C) Chimeric mice were evaluated at 9-d post-ligature placement; alveolar bone loss identified of chimeric mice was not different between mice chimeras. Each symbol represents one mouse. Error bars, se; ns, not significant. D) Bone marrow derived macrophages from WT and Ifi204−/− mice were cultured, primed with LPS, and transfected with poly(dA:dT) (Aim2 activation), interferon stimulatory DNA (ISD), or treated with nigericin to activate the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Supernatant was evaluated by ELISA. n=5 mice/group. Each symbol represents one mouse. Error bars, s.e.
