Figure 6. H151 treatment reduces acute lung injury and apoptosis after intestinal I/R.
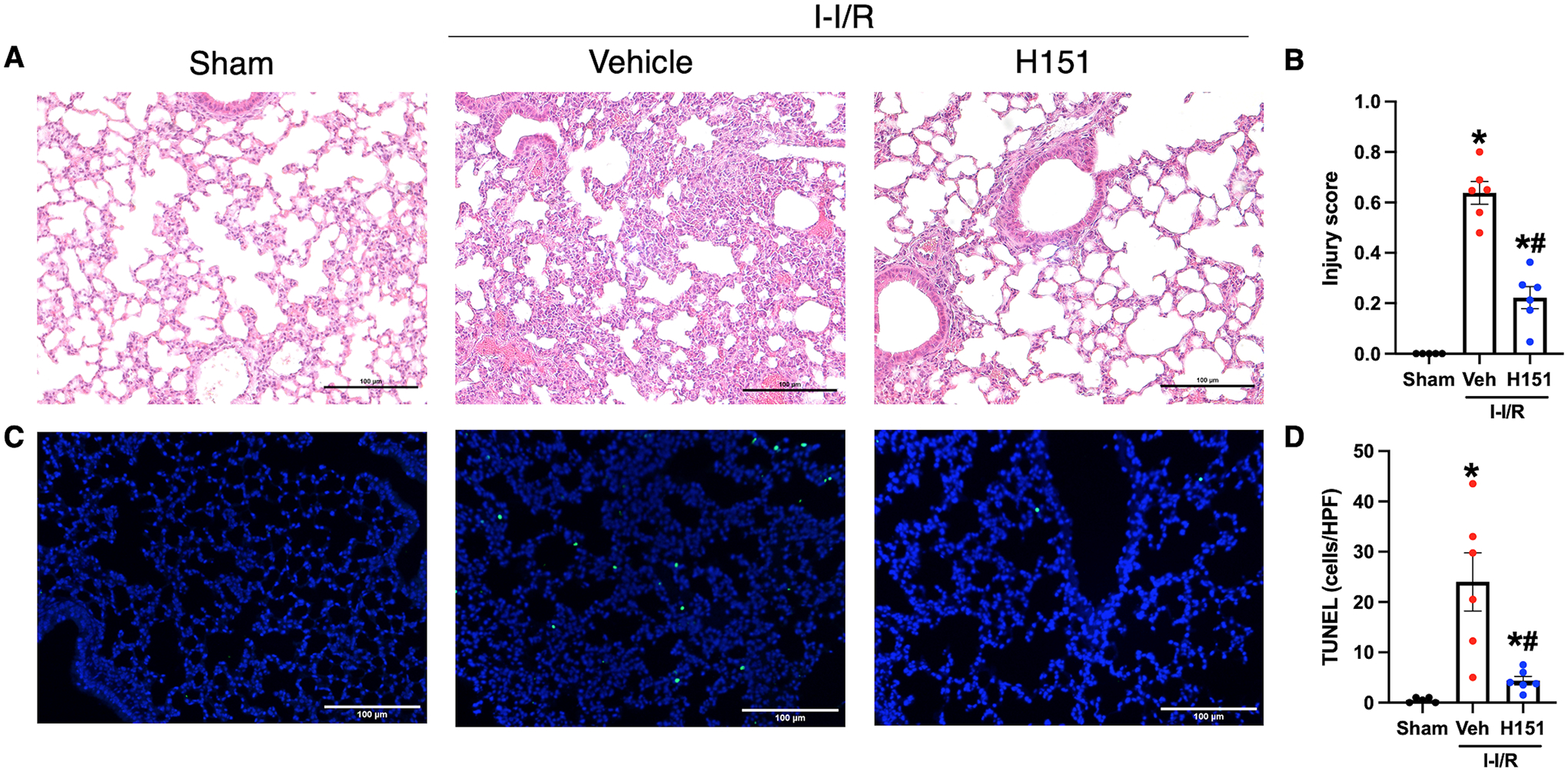
Histological analysis was performed on H&E stained sections of lung tissue, and acute lung injury was assessed using a validated grading scale. (A) Representative images of H&E stained lung tissue at 200x (scale bar: 100μm). (B) Acute lung injury score calculated from zero to one with greater scores reflecting greater injury, taking into consideration proteinaceous debris in the airspaces, thickening of alveolar septa, presence of hyaline membranes, and lymphocytic infiltration (n = 5–6/group). TUNEL staining of lung tissue sections was performed to evaluate cell death. (C) Representative images of TUNEL stained sections at 100x. Scale bar: 100μm. (D) TUNEL-positive cells were quantified using ImageJ software and are expressed as cells/HPF (n = 5–6/group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and compared by (B) ANOVA and SNK tests, and (D) Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA (*p < 0.05 vs sham, #p < 0.05 vs vehicle). I-I/R, intestinal-ischemia/reperfusion.
