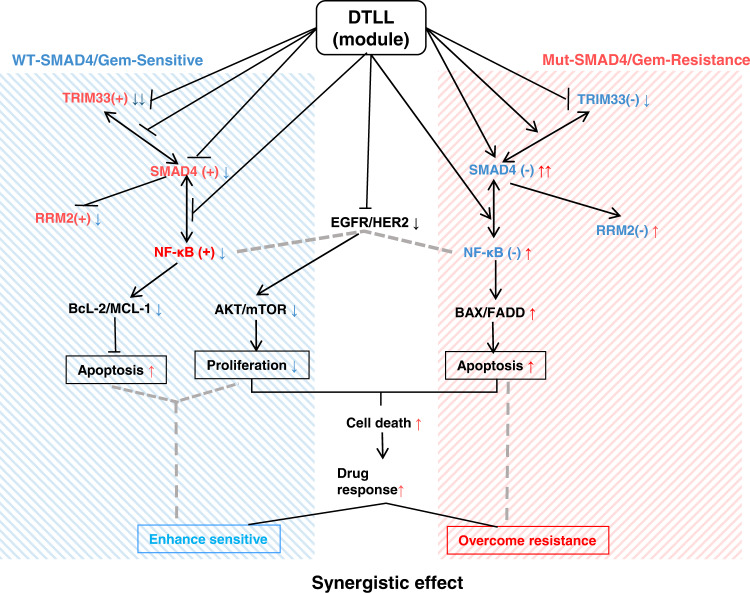
Fig. 9. Schematic illustration model of the DTLL action mechanism along with mutant and wild-type SMAD4 in PDAC cells.
There were different action mechanisms of mutant and wild-type SMAD4 on the PDAC drug response with/without DTLL induction. The SMAD4 genetic status of PDAC is responsible for SMAD4 protein levels which determine different cellular susceptibilities. DTLL seems to act as a module of the SMAD4 driver that normalizes its function as a tumor suppressor according to SMAD4 level and genetic status in PDAC, and then adjusts NF-κB, TRIM33, gemcitabine-metabolic enzymes (such as RRM2) and proteomic profiles of PDAC cells, which explains the synergistic effect on tumor growth of DTLL in combination with gemcitabine. Specifically, DTLL contributes to decreases mainly in AKT/mTOR signaling and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2 and MCL1) by impaired NF-κB function in WT-SMAD4/GEM-sensitive PDAC cells. However, DTLL predominantly enhances the expression of apoptotic BAX and FADD by restoring SMAD4 bioactivity to trigger downstream NF-κB-regulated signaling in Mut-SMAD4/GEM-resistant cells. Moreover, NF-κB expression was regulated as a SMAD4 target in these two types of cells, and the interaction between these two proteins was different in an opposite direction. In addition, SMAD4 status significantly impacted the proteomic profiles, especially RRM2 expression. As a result, DTLL in combination with chemotherapeutic agents shows synergistic effects by either enhancing sensitivity or overcoming resistance in PDAC cells via wild-type or mutant SMAD4-mediation, respectively. Note: WT indicates wild type and Mut represents mutant (R100T mutation) SMAD4. (+), sufficient expression; (−), deficient expression.