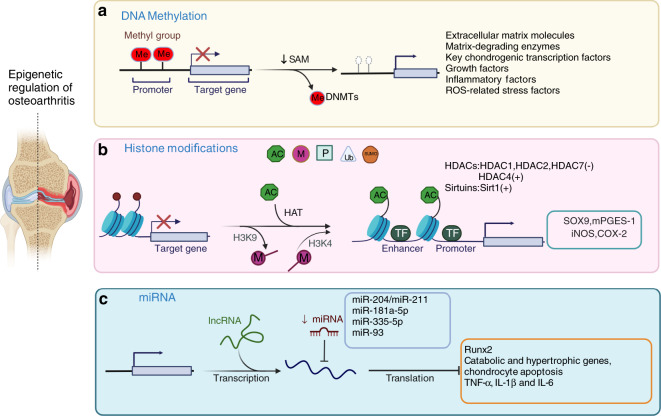
Fig. 1.
Epigenetic regulation of osteoarthritis. Three types of epigenetic regulation of the molecular pathogenesis of OA. a DNA methylation is catalyzed by DNMTs, and abnormal changes in DNA methylation occur in the promoter regions of related genes and signaling pathways in OA chondrocytes. b Histone modifications included phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and SUMOylation. Histone acetylation is mainly mediated by HATs, and histone deacetylation is usually catalyzed by two types of enzymes: classic histone deacetylases (HDACs) and sirtuins. Increased H3K4 methylation leads to catabolic responses mediated by iNOS and COX-2 expression in human OA chondrocytes. The methylation of H3K9 increases Sox9 and mPGES-1 expression in human OA chondrocytes. c MiR-204/miR-211, miR-181a-5p, miR-335-5p, and miR-93 inhibit Runx2, chondrocyte apoptosis, and the expression of catabolic and hypertrophic genes