Fig. 3.
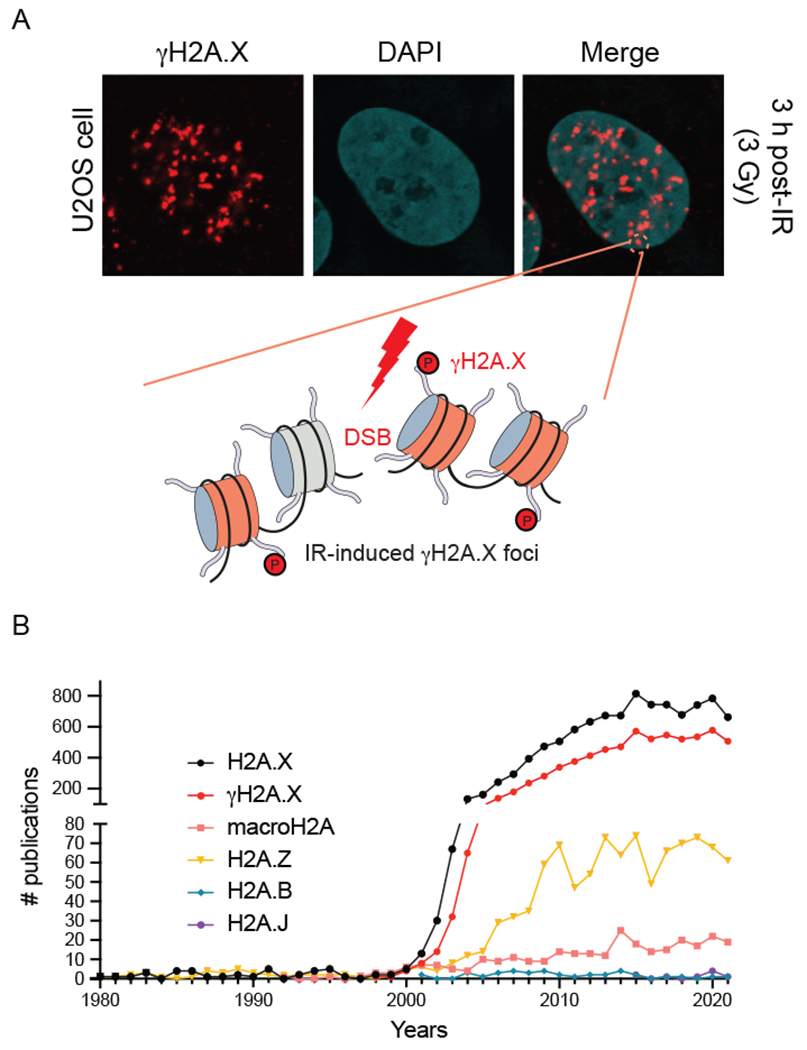
Characterization of γH2A.X and histone H2A variant publications. (a) Ionizing radiation-induced γH2A.X foci. Human U2OS cancer cells treated with IR and analyzed by immunofluorescence with a γH2A.X specific antibody (image provided by Doohyung Lee, Miller lab, UT Austin). Each focus represents γH2AX signal surrounding an individual DNA double-strand break. γH2AX-modified nucleosomes are highlighted in red and unmodified nucleosomes are in gray. (b) Analysis of publications involving histone H2A variants. H2A.X is the most highly studied histone H2A variants, with the majority of publications involving γH2A.X.
