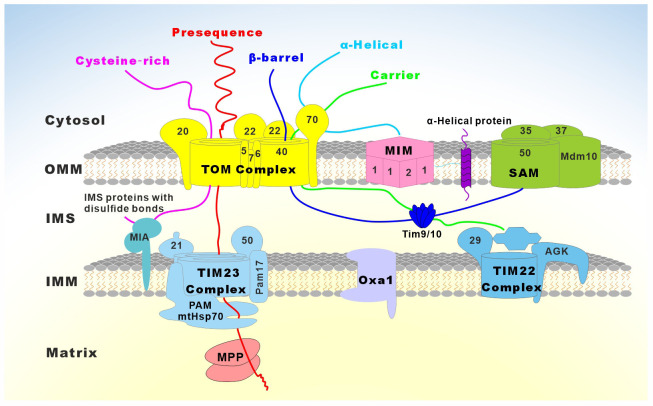
Figure 6.
Overview of the major mitochondrial protein import pathways. Mitochondrial precursor proteins are synthesized in the cytosol, transported to the mitochondria, and directed to the correct mitochondrial compartments. Five major protein import pathways have been identified so far: (1) Presequence-carrying preproteins are imported through the translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane (TOM) and the translocase of the inner mitochondrial membrane (TIM23) complexes. Proteins containing a hydrophobic sorting signal are released into the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), while hydrophilic proteins are imported into the matrix with the help of the presequence translocase-associated motor (PAM) complex. Membrane potential across the IMM is essential for the entry of presequences into the matrix. The presequences are cleaved by the mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP) and additional proteolytic processing occurs by intermediate cleaving peptidases. Presequence-carrying precursors that are integrated into the IMM are either directly released from the TIM23 complex or transported into the matrix, followed by further insertion into the IMM with the help of Oxa1; (2) Cysteine-rich proteins of the intermembrane space (IMS) are imported by TOM and the mitochondrial IMS import and assembly (MIA) system, which inserts disulfide bonds in the imported proteins; (3) The precursors of β-barrel proteins are translocated through the TOM complex to the TIM9/10 in the IMS and are inserted into the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) by the sorting and assembly machinery (SAM); (4) The precursors of metabolite carriers of the IMM are imported via the TOM complex, small TIM9/10 chaperones, and the carrier translocase TIM22 complex; and (5) Some proteins with α-helical transmembrane segments are inserted into the OMM by the mitochondrial import (MIM) complex.