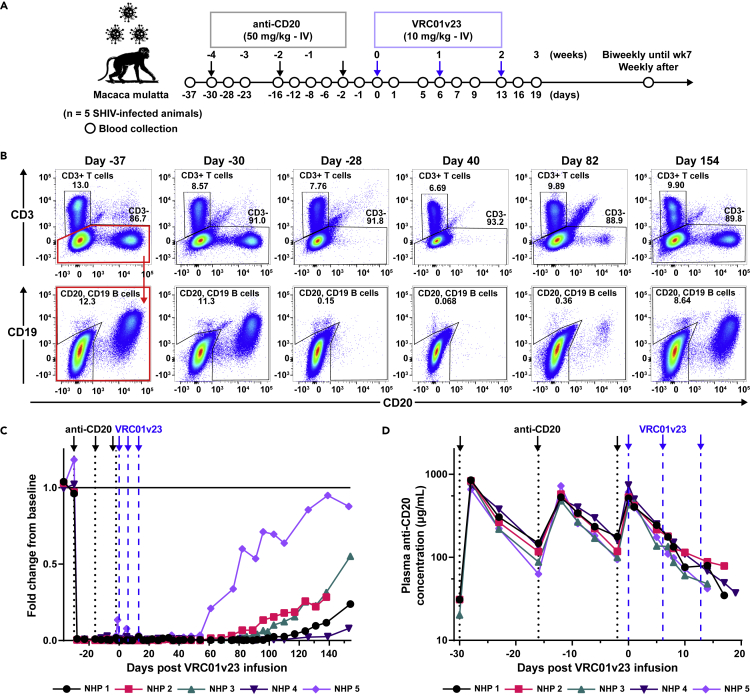
Figure 1.
Study design and in vivo B cell depletion after anti-CD20 infusion
(A) SHIV-infected rhesus macaques were treated with intravenous (IV) infusions of 50 mg/kg afucosylated rhesusized anti-CD20 (anti-CD20, black arrows) followed by 10 mg/kg of bNAb VRC01v23 (blue arrows). Blood was sampled at indicated timepoints over the course of the study.
(B) Representative flow cytometry plots of whole blood CD20+ B cells and total CD3+ T cells at days -37, -30, -28, 40, 82, and 154 of VRC01v23 infusion in NHP 3. B cell counts determined by number of CD19+ and/or CD20+ events after gating on CD3− leukocytes. Peripheral B cell depletion was already seen 2 days following first anti-CD20 infusion.
(C) CD19+ and/or CD20+ B cell counts in whole blood obtained by flow cytometry for each macaque normalized to its CD19+ and/or CD20+ B cell count average from day –37 and day 30 of bNAb infusion, prior to CD20 depletion (black arrows/dotted lines = anti-CD20 infusions, blue arrows/dashed lines = VRC01v23 infusions).
(D) Pharmacokinetics (PK) of anti-CD20 in macaque plasma following three 50 mg/kg IV infusions (LOD = 31 μg/mL). See also Figures S1 and S2.