Fig. 1.
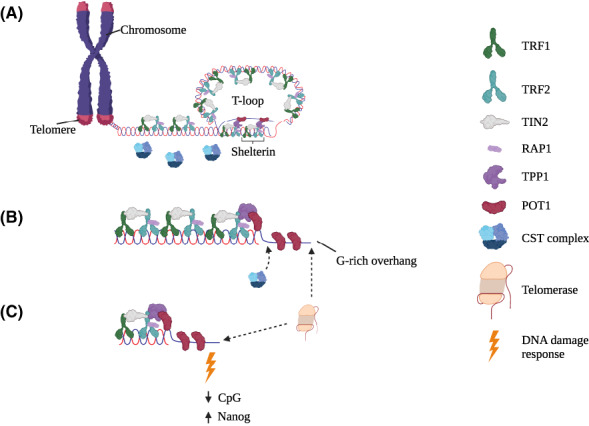
Overview of mammalian telomere structure. (A) Schematic representation of the chromosome end, or telomere in mammals. Telomeric DNA is composed of the hexanucleotide sequence TTAGGG with a single stranded G‐rich 3′ overhang that is looped back into the telomeric DNA to form a telomeric loop (T‐loop). The shelterin complex (composed of the proteins TRF1, TRF2, TIN2, RAP1, TPP1 and POT1) protects telomeres from being recognized as a DNA double‐stranded break. (B) During the S‐phase of the cell cycle, the T‐loop is opened and the G‐rich strand becomes accessible for extension by telomerase. After telomerase has extended the G‐rich strand, the CST complex (composed of the subunits CTC1, STN1, TEN1) together with the DNA replication machinery carries out fill‐in DNA synthesis of the complimentary C‐rich strand. (C) Critically short telomeres exhibit defects not only in telomere integrity (due to a DNA damage response) but can also perturb the epigenetic state (reducing CpG methylation and increasing Nanog expression). [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
