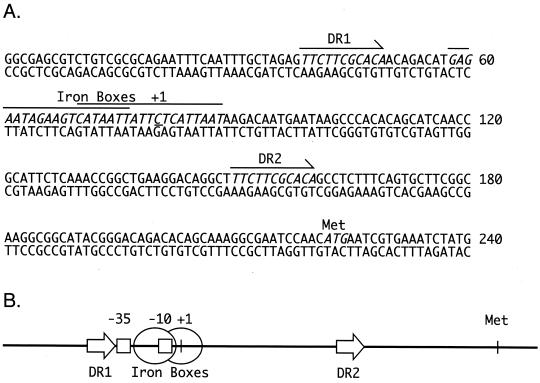
FIG. 5.
The alc operon control region of B. bronchiseptica B013N. (A) Nucleotide sequence of a 240-bp DNA segment representing nucleotide positions −79 to +161 with respect to the alc operon major transcription initiation site (underlined C residue designated +1) (26). Key nucleotide sequence features are italicized. Overlapping nucleotide sequences with similarity to Fur-binding sites (Iron Boxes) are overlined. Two copies of an 11-nucleotide direct repeat sequence (5′-TTCTTCGCACA-3′), designated DR1 and DR2, occupy nucleotide positions −41 to −31 and +71 to +81. The predicted translation initiation methionine (Met) codon for alcA is indicated. (B) Simplified schematic representation of the 240-bp region shown in panel A, showing the spatial relationships of known and predicted regulatory elements. Direct repeat sequences DR1 and DR2 (arrows) and Fur-binding sites (Iron Boxes, designated by ovals) are shown in relation to the major alc operon −35 and −10 promoter determinants (squares) and the transcription initiation site (+1). The relative position of the proposed alcA translation initiation codon (Met) is also indicated.